Passage Obstructive Respiratory Illnesses Are Characterized by an Increased Difficulty Exhaling
Passage
Obstructive respiratory illnesses are characterized by an increased difficulty exhaling much of the air in the lungs. Asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are two of the most common obstructive respiratory illnesses. Asthma is due to allergen hypersensitivity and can be identified by temporary airway inflammation, which causes the bronchioles to narrow. The decreased airway diameter increases the resistance to airflow. Subsequently, air becomes "trapped" in the lungs, restricting the amount of air that can be moved in each breath.COPD refers to a spectrum of disorders and can be a result of emphysema, the irreversible destruction of pulmonary tissue. The breakdown of elastic proteins in the lungs results in a loss of pulmonary resiliency and chronic lung hyperinflation. Because the walls between individual alveoli are broken down, the alveolar sacs that remain are larger.Lung diseases can be diagnosed and monitored using spirometry. A spirometer measures the flow rate and volume of inhaled and exhaled air. In one pulmonary test, a patient is asked to exhale forcibly and completely into a spirometer after maximum inhalation. This test is done to measure the patient's forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) and forced vital capacity (FVC) , the total amount of air exhaled in a single breath.
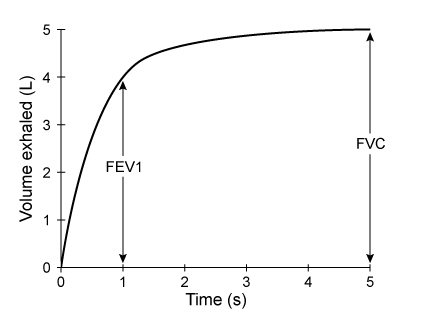 Figure 1 Forced expiratory spirogram of a healthy individual
Figure 1 Forced expiratory spirogram of a healthy individual
Adapted from T. Barreiro, "An Approach to Interpreting Spirometry." American Family Physician. ©2004 AAFP.
-The regulation of respiratory rate is normally most sensitive to:
A) PO2 in the blood.
B) PCO2 in the blood.
C) PO2 in the alveoli.
D) PCO2 in the alveoli.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q62: Passage
Mitochondria are thought to have been independent
Q63: Passage
Obstructive respiratory illnesses are characterized by an
Q64: Passage
Obstructive respiratory illnesses are characterized by an
Q65: Passage
Alzheimer disease (AD) is a progressive condition
Q66: Passage
Mitochondria are thought to have been independent
Q68: Passage
Alzheimer disease (AD) is a progressive condition
Q69: Passage
Mitochondria are thought to have been independent
Q70: Passage
Obstructive respiratory illnesses are characterized by an
Q71: Passage
Eukaryotic organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts
Q72: Passage
Mitochondria are thought to have been independent
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents