Passage
Mitochondria are thought to have been independent bacterial organisms that were engulfed and integrated into eukaryotic cells approximately two billion years ago. Most of the mitochondrial genome was lost or transferred into the large central genome of the eukaryotic nucleus, leaving only a residual genome within each mitochondrion.Because multiple mitochondria are found in the cell, mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) mutations result in a condition known as heteroplasmy, or the intracellular mixture of wild-type mtDNA and mutant mtDNA. Just as the cellular ratio of wild-type to mutant mtDNA varies, the overall mtDNA content within a tissue or organ is also highly variable. For this reason, disease-causing mutant mtDNA manifests phenotypically only when the majority of mitochondria within a given tissue express the deleterious allele. In addition, the variability in mtDNA content makes it possible for individuals with the same mitochondrial mutation to display drastically different clinical symptoms.To investigate how heteroplasmy influences disease manifestation, researchers analyzed an A to G substitution at nucleotide 3243 in the tRNAleu gene of mtDNA. This mutation has been associated with hereditary hearing loss, diabetes mellitus, and a syndrome characterized by mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and strokelike episodes.Family members who were confirmed to have the A3243G mutation were tested using an audiometry examination to assess hearing impairment, as shown in Table 1. The subjects carried no other genetic mutations known to cause hearing loss.Table 1 Audiometry Results From Family Members with the A3243G Mutation
 The blood samples of these subjects were collected, and the 3243 region of the tRNAleu gene was amplified via standard PCR. The PCR products were subsequently treated with the restriction enzyme ApaI and visualized on a PAGE gel. The normal undigested PCR product is 161 bp in length, but the PCR product amplified from the mutant A3243G is digested into two fragments by ApaI.
The blood samples of these subjects were collected, and the 3243 region of the tRNAleu gene was amplified via standard PCR. The PCR products were subsequently treated with the restriction enzyme ApaI and visualized on a PAGE gel. The normal undigested PCR product is 161 bp in length, but the PCR product amplified from the mutant A3243G is digested into two fragments by ApaI.
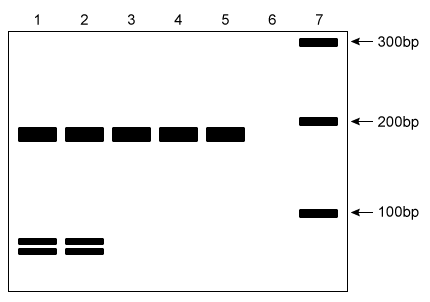 Figure 1 PAGE visualization of PCR products following ApaI digestion
Figure 1 PAGE visualization of PCR products following ApaI digestion
Adapted from Hadjivasiliou Z, Pomiankowski A, Seymour RM, Lane N. Selection for mitonuclear co-adaptation could favour the evolution of two sexes. Proc Biol Sci. 2012;279(1734) :1865-72.
-Based on the passage, which of the following reagents was most likely used during PCR?
A) Free ribonucleoside triphosphates
B) RNA polymerase
C) A template sequence containing deoxyribonucleotides
D) Primer pairs with minimal GC content
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q67: Passage
Obstructive respiratory illnesses are characterized by an
Q68: Passage
Alzheimer disease (AD) is a progressive condition
Q69: Passage
Mitochondria are thought to have been independent
Q70: Passage
Obstructive respiratory illnesses are characterized by an
Q71: Passage
Eukaryotic organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts
Q73: Passage
Eukaryotic organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts
Q74: Passage
Obstructive respiratory illnesses are characterized by an
Q75: Passage
Alzheimer disease (AD) is a progressive condition
Q76: Passage
Eukaryotic organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts
Q77: Passage
Mitochondria are thought to have been independent
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents