Passage
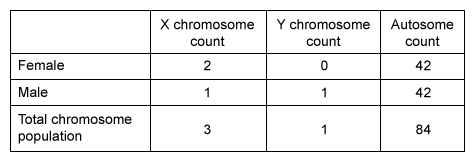
The sex chromosomes X and Y are involved in mammalian sex determination. Organisms with two wild-type (WT) X chromosomes develop as females (XX) , but those with a combination of WT X and Y chromosomes develop as males (XY) (Table 1) . Both sexes also inherit a set of autosomes (nonsex chromosomes) . Humans inherit 22 pairs of autosomes (44 total) . In contrast, rabbits inherit 21 pairs of autosomes (42 total) .Table 1 Chromosome Types Inherited by a Male and Female Rabbit (Note: The Y chromosome has fewer alleles than the X chromosome.)
 Specifically, the SRY gene, located on the mammalian Y chromosome, is crucial for male sex determination and induction of testis development. Studies in mammals have shown that regardless of an organism's combination of sex chromosomes, fetuses will always develop as female in the absence of the SRY protein. In addition, one of the X chromosomes becomes inactivated in WT,XX females to prevent them from having double the amount of X-chromosome gene products as WT,XY males.Sp1 is a transcription factor with demonstrated regulatory control of SRY gene expression, and XY individuals with mutations affecting the Sp1 binding site on the SRY gene have been shown to develop female sex characteristics. Unlike SRY, the gene for Sp1 is located on an autosome.Researchers knocked out (KO) Sp1 binding sites on the SRY gene in rabbit embryos (Sp1 KO,XY rabbits) and observed their sexual development following implantation in surrogate mothers. The relationship between the SRY gene and sexual development can be explained by the following experimental observations: Most Sp1 KO,XY rabbits had female genitalia and displayed normal mating behaviors.
Specifically, the SRY gene, located on the mammalian Y chromosome, is crucial for male sex determination and induction of testis development. Studies in mammals have shown that regardless of an organism's combination of sex chromosomes, fetuses will always develop as female in the absence of the SRY protein. In addition, one of the X chromosomes becomes inactivated in WT,XX females to prevent them from having double the amount of X-chromosome gene products as WT,XY males.Sp1 is a transcription factor with demonstrated regulatory control of SRY gene expression, and XY individuals with mutations affecting the Sp1 binding site on the SRY gene have been shown to develop female sex characteristics. Unlike SRY, the gene for Sp1 is located on an autosome.Researchers knocked out (KO) Sp1 binding sites on the SRY gene in rabbit embryos (Sp1 KO,XY rabbits) and observed their sexual development following implantation in surrogate mothers. The relationship between the SRY gene and sexual development can be explained by the following experimental observations: Most Sp1 KO,XY rabbits had female genitalia and displayed normal mating behaviors.
Sp1 KO,XY rabbits had significantly smaller ovaries and fewer follicles than WT,XX rabbits.
No significant differences were observed in the cervix and uterus between Sp1 KO,XY and WT,XX rabbits.
There was significantly reduced SRY expression in Sp1 KO,XY rabbits when compared to WT,XY males.
WT,XY male rabbits had significantly higher testosterone levels when compared to Sp1 KO,XY rabbits.
Sp1 KO,XY rabbits were infertile when mated with WT,XY males.
Sp1 KO,XY rabbits could become pregnant via embryo transfer.
Song Y et al. Mutation of the Sp1 binding site in the 5' flanking region of SRY causes sex reversal in rabbits. Oncotarget. 2017; 8(24) :38176-83.
-In an isolated population of 10,000 rabbits, 900 are homozygous for a recessive mutant Sp1 allele. Given this, what is the percentage of rabbits in the population who carry the mutant Sp1 allele but do not express the mutant phenotype? (Note: Assume the population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.)
A) 9%
B) 21%
C) 42%
D) 70%
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q221: Passage
The sex chromosomes X and Y are
Q222: Passage
Endometriosis is a chronic, treatable disease of
Q223: Passage
Bone remodeling is the continuous, microscopic process
Q224: Passage
Endometriosis is a chronic, treatable disease of
Q225: The DNA of telomeres can be most
Q227: Passage
The adrenal glands are divided into two
Q228: Passage
Endometriosis is a chronic, treatable disease of
Q229: Passage
The sex chromosomes X and Y are
Q230: Passage
Endometriosis is a chronic, treatable disease of
Q231: Passage
Bone remodeling is the continuous, microscopic process
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents