Passage
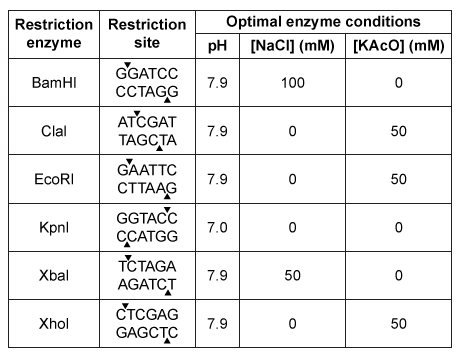
In the central nervous system, myelin produced by oligodendrocytes (glial cells) functions as an insulating sheath surrounding certain nerve fibers. To identify candidate genes involved in the myelination process, researchers collected oligodendrocytes from zebrafish and purified the messenger RNA (mRNA) transcripts expressed by these glial cells. The mRNA was converted to complementary DNA (cDNA) by reverse transcriptase, and the cDNA was fluorescently labeled and assessed for hybridization on a microarray. The expression of mRNA in other zebrafish cells was similarly measured.Transcripts detected in zebrafish oligodendrocytes at levels greater than 3 times those found in other cells were selected as candidate myelination genes. Some of the detected genes, including plp1a, Sox10, and mbp, were previously known to be specific to oligodendrocytes, validating the procedure. The cDNA of newly identified candidates was amplified by PCR, and the ends were digested with the restriction enzymes EcoRI and XhoI. Genes were then ligated into the multiple cloning site (MCS) of the pSKII vector, shown in Figures 1 and 2, which had also been digested by EcoRI and XhoI.
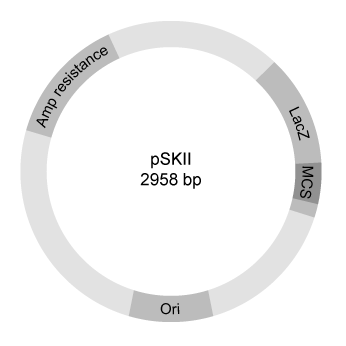 Figure 1 Overview of the pSKII vector (plasmid)
Figure 1 Overview of the pSKII vector (plasmid)
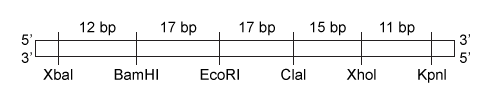 Figure 2 The pSKII MCS, showing the restriction sites of several restriction enzymesTable 1 shows the functional parameters of several restriction enzymes.
Figure 2 The pSKII MCS, showing the restriction sites of several restriction enzymesTable 1 shows the functional parameters of several restriction enzymes.
 To confirm that the candidate genes originated in oligodendrocytes, complementary RNA (cRNA) strands were synthesized from the cloned plasmids and hybridized to fixed zebrafish sections. One of the genes that localized to oligodendrocytes, known as cldnk, produces a 915 base pair mRNA transcript from two exons. The cldnk gene is involved in tight junction formation and may be required for myelin sheath development around axons.
To confirm that the candidate genes originated in oligodendrocytes, complementary RNA (cRNA) strands were synthesized from the cloned plasmids and hybridized to fixed zebrafish sections. One of the genes that localized to oligodendrocytes, known as cldnk, produces a 915 base pair mRNA transcript from two exons. The cldnk gene is involved in tight junction formation and may be required for myelin sheath development around axons.
-Which experiment could confirm that the cldnk gene product is required for myelination?
A) Compare myelin formation in wild-type zebrafish to formation in zebrafish that overexpress cloned cldnk
B) Overexpress cldnk in zebrafish cells other than oligodendrocytes and observe whether those cells produce myelin
C) Compare myelin formation in wild-type zebrafish to that in zebrafish with cldnk knocked out
D) Overexpress a form of cldnk that inhibits the wild-type gene in cells other than oligodendrocytes and observe whether myelin forms
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q293: Several techniques have been developed to treat
Q294: A male African clawed frog (Xenopus laevis)
Q295: A male patient was born with an
Q296: Passage
In the central nervous system, myelin produced
Q297: Scientists studying evolution in yeast found that
Q299: Passage
Within the Actinopterygii (bony fish) lineage, marine
Q300: Bacteria are removed from lymph and blood
Q301: Passage
The heart is a muscular organ comprising
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents