Passage
The heart is a muscular organ comprising four chambers, two atria and two ventricles, that function synergistically to pump blood through a vast, closed network of blood vessels. The chambers are separated by membranous muscular barriers known as septa. Oxygenated blood returning from the lungs via the pulmonary veins fills the left atrium and enters the left ventricle, which then pumps the blood into the systemic arteries to supply other organs in the body. By contrast, deoxygenated blood returning from systemic veins first enters the right atrium, then the right ventricle, and is ultimately siphoned into the pulmonary arteries leading to the lungs. The necessary oxygen, nutrient, and waste exchange occurs between the thinnest blood vessels (capillaries) and neighboring tissues of the systemic and pulmonary circuits.Blood flow throughout the circulatory system is dictated by blood (hydrostatic) pressure, vascular resistance (force opposing blood flow through a vessel) , and cardiac output (blood volume expelled from the ventricles per unit time) . When blood traverses a vessel, it exerts hydrostatic pressure on the vessel walls, which results in the forced movement of fluid out of the vessel and into the interstitial space. The circulating plasma proteins cause the osmotic pressure within the vessel to be higher than that of the interstitial fluid. In turn, osmotic pressure causes fluid to flow from the interstitial space into the blood vessel, opposing hydrostatic pressure.Cardiac output depends in part on heart rate, which is tightly regulated by the sinoatrial (SA) and atrioventricular (AV) nodes, specialized groups of self-depolarizing cells located in the upper right atrial wall and lower interatrial septum, respectively. Action potentials (APs) generated by SA nodal cells stimulate atrial contraction as they travel to the AV node. The AV node delays AP transmission to ventricular cells, ensuring ventricular filling is complete prior to heart contraction.A 63-year-old male patient collapsed while exercising and was hospitalized. The patient presented with an elevated heart rate, low systemic blood pressure, and abnormally low blood oxygen levels. In addition, x-rays revealed excess fluid in his lungs.
-The attending physician orders an electrocardiogram (ECG) to measure the electrical activity of the patient's heart. The results of the ECG of a healthy individual at rest (A) and the ECG of the patient at rest (B) are shown below. 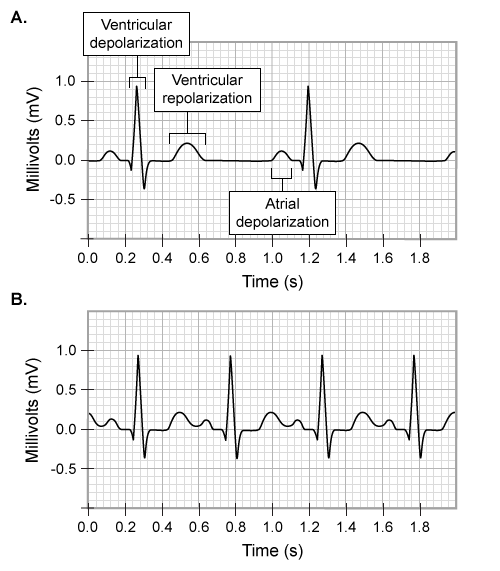 Which of the following conclusions regarding the patient's cardiac function is best supported by these results?
Which of the following conclusions regarding the patient's cardiac function is best supported by these results?
A) Atrial contraction occurs less frequently in the patient than in the healthy individual.
B) APs are fired less frequently from AV nodal cells in the patient than in the healthy individual.
C) Ventricular depolarization occurs for a longer time period in the patient than in the healthy individual.
D) Influx of positive ions into SA nodal cells occurs more rapidly in the patient than in the healthy individual.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q296: Passage
In the central nervous system, myelin produced
Q297: Scientists studying evolution in yeast found that
Q298: Passage
In the central nervous system, myelin produced
Q299: Passage
Within the Actinopterygii (bony fish) lineage, marine
Q300: Bacteria are removed from lymph and blood
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents