Passage
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) interprets the nuclear relaxation or relaxivity of hydrogen nuclei in resident water molecules. Hydrogen nuclei in water have two magnetic spin states: alpha and beta. In the presence of an applied magnetic field, these spins will align with the field in an "excited" state and then relax back to the "ground" state, producing a signal with intensity proportional to relaxivity. Frequently, an MRI contrast agent is used to increase the relaxation time in coordinated molecules, resulting in a more intense signal.Commonly used contrast agents include gadolinium-based agents. Depending on its environment, gadolinium (Gd) can have eight or nine sites in its coordination sphere, allowing Gd3+ to interact with eight water molecules as in Gd(H2O) 83+. The electronic configuration of gadolinium is shown in Figure 1.
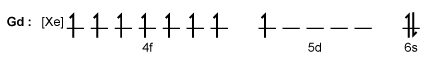 Figure 1 Electronic configuration of gadoliniumGd3+ alone is toxic to cells because its ionic radius is similar to that of Ca2+, allowing Gd3+ to displace Ca2+ in biologically important settings. Therefore, Gd3+ must be coordinated to an organic ligand such as 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA) to allow it to pass through the body safely. When chelated, DOTA displaces the water around gadolinium and leaves only one coordination site for a water molecule (Figure 2) .
Figure 1 Electronic configuration of gadoliniumGd3+ alone is toxic to cells because its ionic radius is similar to that of Ca2+, allowing Gd3+ to displace Ca2+ in biologically important settings. Therefore, Gd3+ must be coordinated to an organic ligand such as 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA) to allow it to pass through the body safely. When chelated, DOTA displaces the water around gadolinium and leaves only one coordination site for a water molecule (Figure 2) .
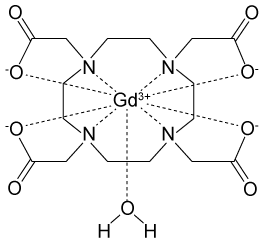 Figure 2 Gd-DOTA with a water coordinated to Gd3+Zinc ions (Zn2+) are required to store insulin and are co-released when insulin is secreted by the pancreas. To detect zinc ions in the body, researchers have designed a variation of Gd-DOTA called Gd-daa3 with two diaminoacetate (daa) arms that preferentially bind to Zn2+ ions (Figure 3) . When Zn2+ is absent, these arms coordinate to Gd3+ and create a nine-coordinate complex that prohibits water from binding to Gd3+. Binding of diaminoacetate arms to Zn2+ frees Gd3+ to coordinate with water molecules. This configuration results in increased signal intensity in the parts of the cell where Zn2+ is located.
Figure 2 Gd-DOTA with a water coordinated to Gd3+Zinc ions (Zn2+) are required to store insulin and are co-released when insulin is secreted by the pancreas. To detect zinc ions in the body, researchers have designed a variation of Gd-DOTA called Gd-daa3 with two diaminoacetate (daa) arms that preferentially bind to Zn2+ ions (Figure 3) . When Zn2+ is absent, these arms coordinate to Gd3+ and create a nine-coordinate complex that prohibits water from binding to Gd3+. Binding of diaminoacetate arms to Zn2+ frees Gd3+ to coordinate with water molecules. This configuration results in increased signal intensity in the parts of the cell where Zn2+ is located.
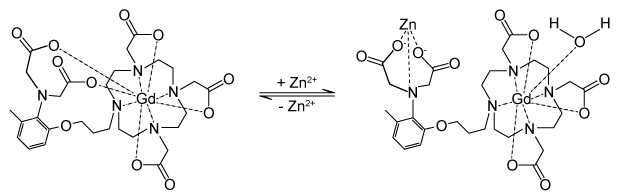 Figure 3 Gd-daa3 when Zn2+ is present
Figure 3 Gd-daa3 when Zn2+ is present
Adapted from Louie A. MRI biosensors: a short primer. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013;38(3) :530-9.
-Gadolinium becomes ionized to Gd3+ when it loses electrons from which orbital(s) ?
A) 4f, 4d, and 5s
B) 4f
C) 4f, 5d, and 6s
D) 5d and 6s
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q7: Passage
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) interprets the nuclear
Q8: Passage
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) interprets the nuclear
Q9: Passage
The bicarbonate (HCO3−) buffer system (Reaction 1)
Q10: Passage
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) interprets the nuclear
Q11: Passage
The bicarbonate (HCO3−) buffer system (Reaction 1)
Q13: Passage
The bicarbonate (HCO3−) buffer system (Reaction 1)
Q14: Passage
Depending on the active compound's specific method
Q15: Passage
Nuclear medicine uses radiopharmaceuticals for disease treatment
Q16: Passage
Depending on the active compound's specific method
Q17: Passage
Nuclear medicine uses radiopharmaceuticals for disease treatment
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents