Passage
Household cleaners commonly contain either ammonia (NH3) or bleach (NaOCl) as the principal active ingredient. Mixing ammonia-based and bleach-based cleaners can be hazardous, as the resulting reactions can form several toxic products. One of these reactions forms the irritant dichloramine (NHCl2) as follows:
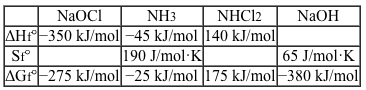
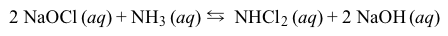 Reaction 1The overall reaction has a standard enthalpy change of −55 kJ/mol and a standard entropy change of −150 J/mol·K. Partial thermodynamic data for formation of Reaction 1 reagents from their elements are shown in Table 1.Table 1 Partial Data for Enthalpies, Entropies, and Free Energies of Formation of Several Compounds at 25 °C
Reaction 1The overall reaction has a standard enthalpy change of −55 kJ/mol and a standard entropy change of −150 J/mol·K. Partial thermodynamic data for formation of Reaction 1 reagents from their elements are shown in Table 1.Table 1 Partial Data for Enthalpies, Entropies, and Free Energies of Formation of Several Compounds at 25 °C
 After it is formed, dichloramine readily enters the gas phase, where it may be inhaled. In the lungs, dichloramine reacts with water to produce hydrochloric acid and ammonia, as well as reactive oxygen species. In small doses, these products cause mild irritation, but inhalation of large amounts of chloramines can lead to pneumonitis (inflammation of the lungs) and may require medical intervention.
After it is formed, dichloramine readily enters the gas phase, where it may be inhaled. In the lungs, dichloramine reacts with water to produce hydrochloric acid and ammonia, as well as reactive oxygen species. In small doses, these products cause mild irritation, but inhalation of large amounts of chloramines can lead to pneumonitis (inflammation of the lungs) and may require medical intervention.
Adapted from Trogolo D, Arey JS. Benchmark thermochemistry of chloramines, bromamines, and bromochloramines: halogen oxidants stabilized by electron correlation. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2015;17(5) :3584-98.
-If large amounts of ammonia and bleach were mixed, emergency responders could help stop the reaction by doing which of the following?
A) Mixing sodium hydroxide into the solution
B) Adding ammonia to the solution
C) Removing dichloramine from the solution
D) Evaporating water from the solution
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q57: Passage
Bone growth and remodeling during fracture healing
Q58: Passage
Heme is found in several proteins, including
Q59: Passage
Heme is found in several proteins, including
Q60: Passage
Water is unique in that all three
Q61: Passage
Household cleaners commonly contain either ammonia (NH3)
Q63: Passage
Combustion occurs when an oxidation-reduction reaction takes
Q64: Passage
An automated external defibrillator (AED) is a
Q65: Passage
An automated external defibrillator (AED) is a
Q66: Passage
An automated external defibrillator (AED) is a
Q67: Passage
An automated external defibrillator (AED) is a
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents