Passage
For a person with perfect vision, light from an object is properly refracted by the eye lens to converge on a single point at the retina, forming a clear image of the object. Vision defects result from eye shape abnormalities or errors in the refractive power of the eye lens. Myopia (nearsightedness) occurs when light from a distant object is incorrectly focused in front of the retina. Hyperopia (farsightedness) occurs when light rays from a nearby object are focused beyond the retina.Many optical techniques are available to measure the refractive error of an individual to determine the necessary correction. Photorefraction is a photographic technique often used with young children because it does not require the individual to be still for a lengthy duration. When the patient is looking at the camera, a flash photograph is taken of the eye to determine the amount of light that is reflected off the retina and captured by the camera lens.In healthy eyes, all the light from the flash that enters the eye is reflected off the retina and returns back to the camera's light source. Because the camera lens does not receive this light, the pupil is completely dark in the resulting image. A myopic eye cannot properly focus the light at the retina. Due to the geometry of the eye and its lens, some of the light is reflected to the top portion of the camera lens. The camera captures an image of a pupil with a crescent of light at the top. In a hyperopic eye, the crescent appears at the bottom of the pupil. Ray diagrams for photorefraction are shown in Figure 1.
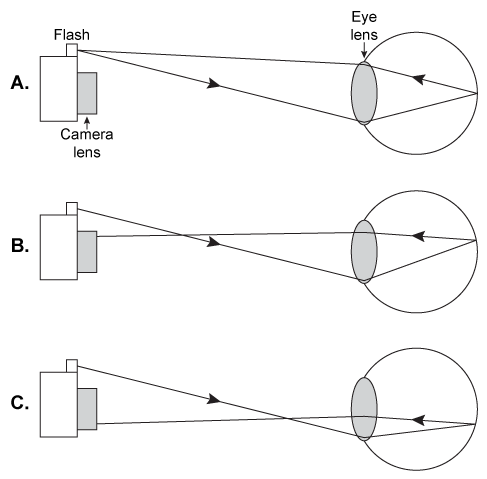 Figure 1 Paths of light in photorefraction for different eyes: (A) Healthy, (B) Myopic, and (C) Hyperopic.
Figure 1 Paths of light in photorefraction for different eyes: (A) Healthy, (B) Myopic, and (C) Hyperopic.
HC. Howland, "Optics of photorefraction: orthogonal and isotropic methods." ©1983 Optical Society of America.
-Myopia can be corrected with a:
A) diverging lens, which creates real and inverted images.
B) diverging lens, which creates virtual and upright images.
C) converging lens, which creates real and inverted images.
D) converging lens, which creates virtual and upright images.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q21: Passage
For a person with perfect vision, light
Q22: Passage
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a
Q23: Passage
The electric capacitance of biological tissues serves
Q24: Passage
The humerus bone in the upper arm
Q25: Passage
The humerus bone in the upper arm
Q27: Passage
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a
Q28: Passage
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a
Q29: Passage
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a
Q30: Passage
The electric capacitance of biological tissues serves
Q31: Passage
For a person with perfect vision, light
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents