Passage
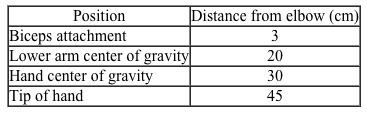
The humerus bone in the upper arm and the radius bone in the lower arm can be modeled as a lever with the elbow joint as the pivot point. Movement about the elbow results from a combination of internal and external forces acting on these bones. The primary internal force is generated from contractions of skeletal muscles; a 1-cm2 cross-sectional area of skeletal muscle can generate a maximum of 7 × 106 dynes of force (1 dyn = 1 g⋅cm/s2) . Friction between the humerus and the radius at the elbow is another internal force that can affect arm movements. As people age, cartilage degeneration decreases the lubrication between bones, which increases the coefficients of static and kinetic friction.The contraction of the biceps, a skeletal muscle in the upper arm, exerts a pulling force on the radius in the lower arm. If the torque generated by this muscle exceeds that of any opposing internal and external forces, the arm curls about the elbow. This specific type of movement is known as a concentric muscle contraction.The following experiments were performed with a 30-year-old male subject. Electrodes were placed around the subject's biceps and attached to an electromyograph, a device that measures the electrical activity of skeletal muscle contractions. The estimated weight of the subject's lower arm is 45 N, and the subject's lower arm segments to the elbow are shown in Table 1.Table 1 Lower Arm Segment Lengths
 Experiment 1The subject kept his entire arm stationary and in a fixed position while holding balls of varying masses. The upper arm was perpendicular to the ground, and the lower arm was parallel to the ground (Figure 1) .
Experiment 1The subject kept his entire arm stationary and in a fixed position while holding balls of varying masses. The upper arm was perpendicular to the ground, and the lower arm was parallel to the ground (Figure 1) .
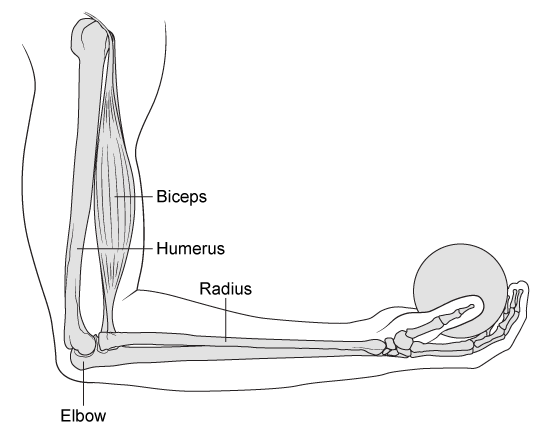 Figure 1 The fixed position of the arm during Experiment 1Experiment 2The subject kept his upper arm stationary and perpendicular to the ground while lifting and lowering balls of varying masses.
Figure 1 The fixed position of the arm during Experiment 1Experiment 2The subject kept his upper arm stationary and perpendicular to the ground while lifting and lowering balls of varying masses.
Adapted from N. Ozkaya, Fundamentals of Biomechanics. (C) 2016 Springer.
-During Experiment 2, the subject lifts a ball with a mass m a vertical distance d1 and then lowers the ball a greater vertical distance d2. What is the net work done by gravity on the ball?
A) W = 0 for all cases because gravity is a conservative force
B) W = mg(d2 − d1) , because gravity does work to lift and lower the ball
C) W = mgd2, because gravity does work only to lower the ball
D) W = mg(d1 + d2) , because gravity does work only on the net vertical path
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q19: Passage
In hemodynamics, blood flow through the cardiovascular
Q20: Passage
During deep underwater dives, scuba divers must
Q21: Passage
For a person with perfect vision, light
Q22: Passage
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a
Q23: Passage
The electric capacitance of biological tissues serves
Q25: Passage
The humerus bone in the upper arm
Q26: Passage
For a person with perfect vision, light
Q27: Passage
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a
Q28: Passage
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a
Q29: Passage
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents