Passage
When present in the bloodstream above a threshold partial pressure, a general anesthetic blocks the sensation of pain, induces a state of unconsciousness, and causes muscle paralysis. Many anesthetic agents are administered in their gaseous phase and are absorbed into the bloodstream through the lungs. The rate of diffusion Vgas of an anesthetic across the alveolar membrane with a surface area A and a thickness T is described by the Fick law of diffusion:
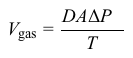 Vgas=DAΔPTEquation 1where D is the diffusion coefficient specific for the gas and ΔP is the partial pressure difference across the membrane.An inhaled anesthetic is described by its blood-gas partition coefficient, the ratio of the anesthetic's concentration in the blood to its concentration in the lungs when the partial pressures are equal. The concentration C of an anesthetic gas dissolved in blood is described by the Henry law of solubility:
Vgas=DAΔPTEquation 1where D is the diffusion coefficient specific for the gas and ΔP is the partial pressure difference across the membrane.An inhaled anesthetic is described by its blood-gas partition coefficient, the ratio of the anesthetic's concentration in the blood to its concentration in the lungs when the partial pressures are equal. The concentration C of an anesthetic gas dissolved in blood is described by the Henry law of solubility:
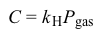 C=kHPgasEquation 2where kH is the solubility constant specific for the gas and Pgas is the partial pressure of the gas.Due to the paralytic effects of general anesthetics, mechanical ventilators are usually necessary to assist a patient's breathing during surgery. Positive-pressure ventilators are noninvasive and use external pumps to induce inspiration by forcing air into the lungs through a ventilation mask. Despite the paralytic effects of general anesthesia, patients are often capable of expiration without the active aid of a mechanical ventilator.
C=kHPgasEquation 2where kH is the solubility constant specific for the gas and Pgas is the partial pressure of the gas.Due to the paralytic effects of general anesthetics, mechanical ventilators are usually necessary to assist a patient's breathing during surgery. Positive-pressure ventilators are noninvasive and use external pumps to induce inspiration by forcing air into the lungs through a ventilation mask. Despite the paralytic effects of general anesthesia, patients are often capable of expiration without the active aid of a mechanical ventilator.
-Which of the following graphs best depicts the anesthetic partial pressure along the length of the pulmonary capillaries when it is first administered?
A) 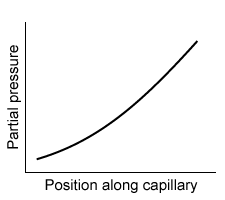
B) 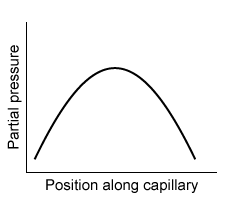
C) 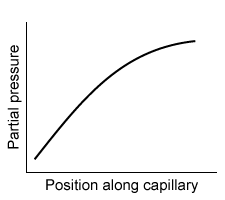
D) 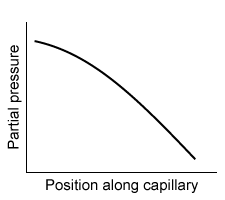
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q50: Passage
The humerus bone in the upper arm
Q51: Passage
The effects of gravity are effectively negated
Q52: Passage
The effects of gravity are effectively negated
Q53: Passage
When present in the bloodstream above a
Q54: Passage
The effects of gravity are effectively negated
Q56: Passage
When present in the bloodstream above a
Q57: Passage
When present in the bloodstream above a
Q58: Passage
The effects of gravity are effectively negated
Q59: Passage
The effects of gravity are effectively negated
Q60: Passage
In mass spectrometry, a sample's molecules are
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents