Passage
In mass spectrometry, a sample's molecules are ionized in a vacuum and then exposed to a uniform electric field created by a high-voltage plate in the acceleration chamber. The electric field accelerates the ions until they arrive at the next section of the device, designated as the separation chamber. In this section, the drifting ions are sorted by their mass-to-charge ratio (m/q) .The separation chamber in a time-of-flight mass spectrometer (TOF-MS) is linear and has no electric or magnetic fields. The ions travel at a constant velocity through the chamber until they reach the detector. The time it takes for an ion to reach the detector depends on its m/q ratio.
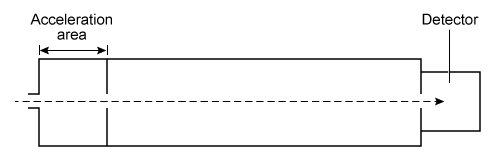 Figure 1 Time-of-flight mass spectrometerA magnetic sector mass spectrometer (MS-MS) has a curved separation chamber where a magnetic field is generated. The magnetic field exerts a centripetal force on drifting ions, bending their trajectories into curved paths. The radius of the curvature depends on the ion's m/q.
Figure 1 Time-of-flight mass spectrometerA magnetic sector mass spectrometer (MS-MS) has a curved separation chamber where a magnetic field is generated. The magnetic field exerts a centripetal force on drifting ions, bending their trajectories into curved paths. The radius of the curvature depends on the ion's m/q.
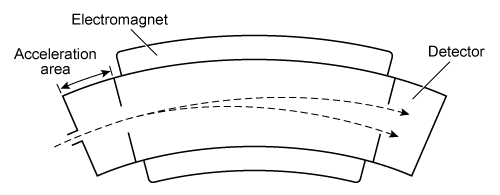 Figure 2 Magnetic sector mass spectrometerThe centripetal force (F) acting on a particle can be determined from its mass (m) and velocity (v) and the radius (r) of the curved path:F = mv2/rEquation 1
Figure 2 Magnetic sector mass spectrometerThe centripetal force (F) acting on a particle can be determined from its mass (m) and velocity (v) and the radius (r) of the curved path:F = mv2/rEquation 1
-What is the force felt by a doubly ionized particle in a 2,000-N/C electric field? (Note: The charge of an electron is e = 1.6 × 10−19 C.)
A) 1.6 × 10−22 N
B) 3.2 × 10−22 N
C) 3.2 × 10−16 N
D) 6.4 × 10−16 N
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q43: Passage
In mass spectrometry, a sample's molecules are
Q44: Passage
When present in the bloodstream above a
Q45: Passage
In mass spectrometry, a sample's molecules are
Q46: Passage
In mass spectrometry, a sample's molecules are
Q47: Passage
The effects of gravity are effectively negated
Q49: Passage
When present in the bloodstream above a
Q50: Passage
The humerus bone in the upper arm
Q51: Passage
The effects of gravity are effectively negated
Q52: Passage
The effects of gravity are effectively negated
Q53: Passage
When present in the bloodstream above a
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents