A branded store has outlets around the world that generates profit in the British pound, the New Zealand kiwi, and the Japanese yen. At the end of each quarter, the store converts the revenue from these three international outlets back into U.S. dollars, exposing itself to exchange rate risk. The current exchange rates are US$1.56 per £1, US$0.85 per NZD$1, and US$0.02 per ¥1. The management of the store wants to construct a simulation model to assess its vulnerability to uncertain exchange rate fluctuations. The quarterly profits earned in British pounds, New Zealand kiwis, and Japanese yen are £150,000, NZD$200,000, and ¥9,000,000, respectively. The data is given below.
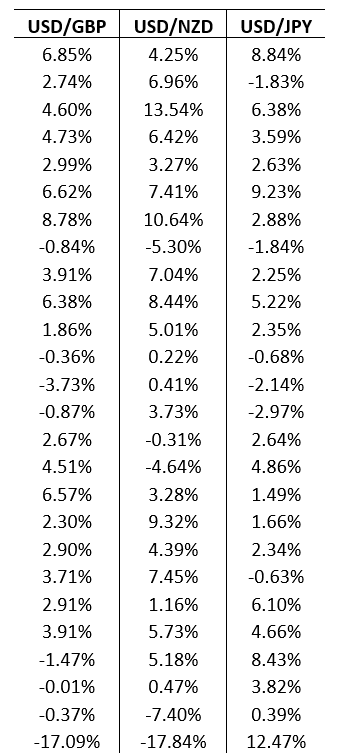
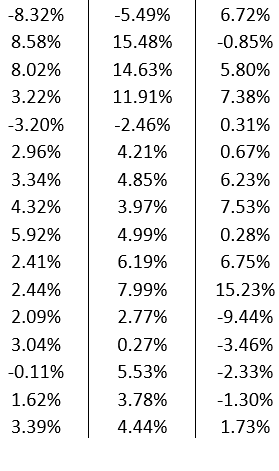
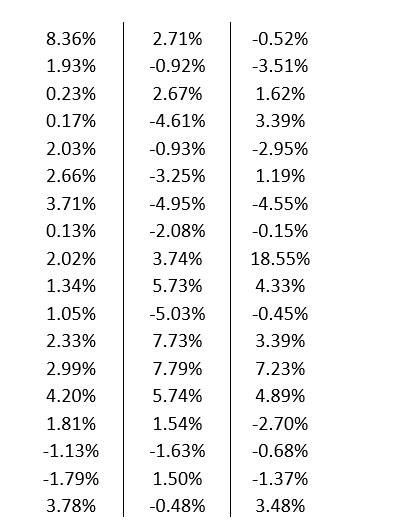
a. If exchange rates stay at their current values, what is the total quarterly profit in U.S. dollars?
b. Model the uncertainty in the quarterly changes of the exchange rates between U.S. dollars and British pounds, New Zealand kiwis, and Japanese yen using a SLURP. Use your simulation model to estimate the average total quarterly profit in U.S. dollars. What is the probability that the total quarterly profit will be lower than the answer in part a?
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q29: All the values of computer-generated random numbers
Q36: The _ function in Excel is used
Q38: The random variables corresponding to the interarrival
Q41: The manager of a company decides to
Q42: Consider the table below with information regarding
Q44: A specialty hedge fund is considering the
Q45: A football tournament is conducted between Team-A
Q45: An Investment firm offers free financial planning
Q47: Sunseel Industries produces different types of raw
Q48: A tourist bus can accommodate 80 people
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents