Secure Strategies. Suppose two competitors, McGraw-Hill, Inc., and Pearson, PLC., each face an important strategic decision concerning whether or not they should boost promotion on new product introductions. McGraw-Hill can choose either row in the payoff matrix defined below, whereas Pearson can choose either column. For McGraw-Hill, the choice is either "boost promotion" or "hold promotion constant." For Pearson, the choices are the same. Notice that neither firm can unilaterally choose a given cell in the profit payoff matrix. The ultimate result of this one-shot, simultaneous-move game depends upon the choices made by both competitors. In this payoff matrix, the first number in each cell is the profit payoff to McGraw-Hill; the second number is the profit payoff to Pearson (in billions).

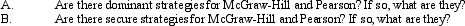
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q27: Limit Pricing. Microsoft Corp. maintains an Internet
Q28: Limit pricing is a competitive strategy to
Q29: The success of market penetration pricing strategies
Q30: Secure Strategies. Imagine two competitors, Microsoft Corp.
Q31: Game Types. Portray each of the following
Q32: Game Types. Distinguish each of the following
Q33: Prisoner's Dilemma. In the classic characterization of
Q34: Game Theory Concepts.
Indicate whether each of
Q35: Game Theory Classifications.
Demonstrate whether each of
Q36: Game Types. Describe each of the following
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents