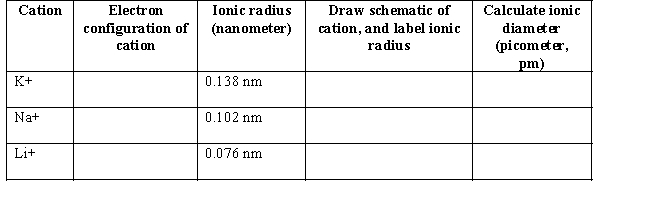
(a) Group I cations are common ions found in organic salts.Write the electron configuration for the Group I cations below.In the fourth column,use circles to represent the relative size of each cation conceptually.Define the term ionic radius and label the ionic radius of each cation.
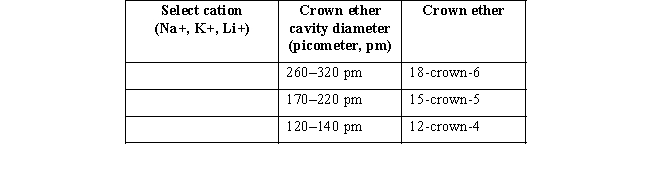
(b) Organic molecules called crown ethers (refer to the box titled "Phase Transfer Catalysts" in Chapter 2 of your text)can sequester a cation of specific size to make the organic anion more reactive.Charles Pedersen,in fact,shared the 1987 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for contributions to the synthesis of crown ethers.Suppose you wanted to use a crown ether to selectively remove each individual cation from a solution of sodium,lithium,and potassium.For each cation,which crown ether might you add?
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q41: Rank N-N-dimethylaniline,phenethylamine,and phenethylamine hydrochloride in order of
Q42: Explain the chemical difference between a detergent
Q43: Which of the following benzene derivatives would
Q44: Propanol can be dissolved in diethyl ether
Q45: Your lab partner disobeyed lab rules and
Q47: Rank 1,4-dimethylbenzene,phenol,and N,N-dimethylaniline in order of decreasing
Q48: Why do polar aprotic solvents solvate cations
Q49: Explain why polar protic solvents (like butanol)solvate
Q50: The solvent tert-butyl methyl ether (MTBE)is used
Q51: Tertiary amides are typically insoluble in water.The
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents