Calculate 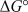 for an electrochemical cell reaction that occurs under basic aqueous conditions based on the following two half-reactions for which the standard reduction potentials are given.Use the smallest whole-number coefficients possible when balancing the overall reaction.
for an electrochemical cell reaction that occurs under basic aqueous conditions based on the following two half-reactions for which the standard reduction potentials are given.Use the smallest whole-number coefficients possible when balancing the overall reaction.
Cd(OH) 2 + 2 e- Cd + 2 OH- -0.824 V
NiO(OH) + H2O + e- Ni(OH) 2 + OH- +1.32 V
A) "-669 kJ"
B) "+95.7 kJ"
C) "-95.7 kJ"
D) "-414 kJ"
E) "+414 kJ"
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q53: The change in free energy for
Q62: An electronic device requires two 1.50-V
Q64: If the potential of a voltaic cell
Q65: Which statement does NOT correctly describe
Q65: The spontaneous redox reaction in a
Q66: Based on the information in the
Q67: In one episode of the 1960s television
Q70: An electronic device requires four 1.50-V
Q72: Based on the information in the
Q74: An electrochemical cell is constructed with
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents