Toxoplasma gondii is a single-celled parasitic protozoan that infects and replicates in macrophages. It is common in the environment, and is transmitted to humans by the ingestion of undercooked meat or by accidental ingestion of the parasite's oocytes from contaminated water or cat litter. Infected individuals with healthy immune systems are generally asymptomatic, and rapidly clear the infection. However, in AIDS patients, infections of Toxoplasma gondii can lead to severe disease and even death. To investigate the immune mechanisms important in controlling Toxoplasma gondii, a mouse model of the infection was developed. Mice were infected with the protozoa at a dose where the majority of the mice survive the infection, and at the same time, were injected with a neutralizing antibody to a cytokine made by T cells (anti-'X' IgG) . A second group of mice received the protozoa plus a control IgG antibody, as shown in Figure Q10) . 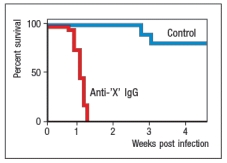 Figure Q10) The most likely candidate for cytokine 'X' is:
Figure Q10) The most likely candidate for cytokine 'X' is:
A) IFN-
B) IL-2
C) IL-4
D) IL-17
E) GM-CSF
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q1: Nitric oxide and superoxide radicals are toxic
Q2: A set of mice are each immunized
Q3: Initially after an infection, the majority of
Q5: Leprosy is a disease caused by the
Q6: IL-23 is a cytokine made by macrophages
Q7: Inflammatory bowel disease (colitis) is a
Q8: Salmonella typhimurium is a Gram-negative bacterial
Q9: Allergic airway inflammation can be induced in
Q10: In addition to producing distinct innate responses
Q11: Immunological memory in humans has been examined
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents