Allergic airway inflammation can be induced in mice by immunizing them with an allergen that produces a TH2 effector response, and then challenging the immunized mice with an inhaled form of that allergen. In this disease model, the TH2 effector cells present in the lung respond to the inhaled allergen challenge by producing type 2 cytokines that recruit eosinophils and induce airway inflammation. In addition, a component of this TH2 response is antigen-independent, as shown by the effects of administering a neutralizing antibody along with the allergen challenge. This neutralizing antibody (anti-'X' IgG) has the effects shown in Figure Q14) . 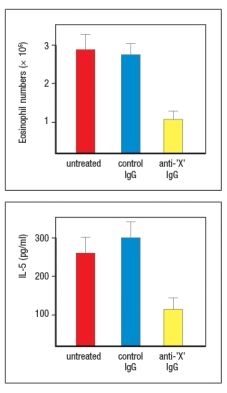 antibody was shown to inhibit the response of the TH2 cells, and therefore is likely to be:
antibody was shown to inhibit the response of the TH2 cells, and therefore is likely to be:
A) A neutralizing antibody to IL-12
B) A neutralizing antibody to IL-4
C) A neutralizing antibody to TSLP
D) A neutralizing antibody to STAT4
E) A neutralizing antibody to IL-13
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q4: Toxoplasma gondii is a single-celled parasitic
Q5: Leprosy is a disease caused by the
Q6: IL-23 is a cytokine made by macrophages
Q7: Inflammatory bowel disease (colitis) is a
Q8: Salmonella typhimurium is a Gram-negative bacterial
Q10: In addition to producing distinct innate responses
Q11: Immunological memory in humans has been examined
Q12: In response to an intracellular bacterial
Q13: Infections of intracellular pathogens (e.g., mycobacteria, listeria,
Q14: In the cases of some infections, such
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents