MPSV-4 is a tetravalent polysaccharide vaccine designed to elicit antibodies to four different serotypes of Neisseria meningitidis, a bacterial infection that causes meningitis and sepsis in susceptible individuals. However, the protection induced by this vaccine is short-lived, and normally wanes to undetectable levels by 2-3 years post-vaccination. In addition, MPSV-4 does not induce mucosal immunity to Neisseria meningitidis; instead, it only protects against bacteria that access the bloodstream. Two newly developed vaccine candidates (A and B) are tested in mice for their ability to elicit high concentrations of anti-meningococcal antibodies that would provide mucosal as well as bloodstream protection. Also, the ideal candidate vaccine should also provide long-lasting immunity to the infection. Figure Q29)A is a diagram of the results from the primary immunization with both candidate vaccines: 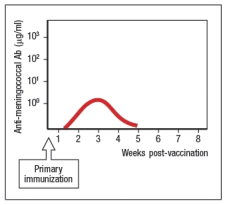
a) what is the predominant antibody isotype elicited by the primary immunization with these candidate vaccines? In which part of the body is that antibody primarily found?
Figure shows the responses to a primary, followed by a secondary immunization to each of the two candidate vaccines. 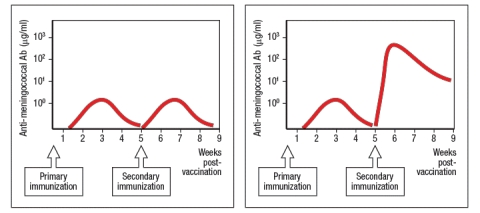
b) Which candidate vaccine elicits the preferred response? What are the three aspects of the preferred response that make it the candidate vaccine of choice?
The vaccine developers refuse to divulge the components of the candidate vaccines A and B.
c) What is the likely composition of each vaccine and what evidence from the information above are used to lead to your conclusions?
d) To confirm the choice of the preferred candidate vaccine, what type of additional information from the vaccine trials in mice shown above would support this conclusion? Name two additional features of the secondary antibody response to each candidate vaccine that could be assessed, and what results would be expected for each of the candidate vaccines.
e) To assess whether either candidate vaccine might provide mucosal immunity in addition to immunity in the bloodstream, what feature of the response to each vaccine should be examined?
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q18: The vaccine to Haemophilus influenzae type b
Q19: Studies show that about 50-100 different B
Q20: Infants born with the immunodeficiency disease X-linked
Q21: The upper respiratory tract of many individuals
Q22: Surprisingly, individuals with defects in the early
Q24: The W/Wv mouse strain is heterozygous for
Q25: IgM antibodies are much more efficient than
Q26: Individuals infected with herpes simplex virus
Q27: Neutralizing antibodies are effective at preventing infection
Q28: Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) is an important
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents