Virus infections induce production of interferons that act on infected cells to enhance their recognition by CD8 cytotoxic T cells. To counter these mechanisms, viruses often encode proteins that interfere with antigen processing and presentation. In an experiment, cells infected with Virus X are treated with interferon and compared with uninfected cells treated with interferon. Proteasomes are isolated from the two cell populations and their enzymatic activities are compared. The data in Figure show the amino acid preferences for cleavage of peptides by the two samples of proteasomes. 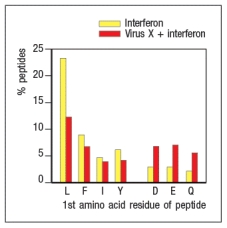
Based on these data, Virus X most likely encodes a protein that interferes with:
A) The expression of MHC class I on the surface of the infected cell
B) The rate at which peptides are produced from intact proteins in the infected cell
C) The transport of peptides from the cytosol to the endoplasmic reticulum in the infected cell
D) The replacement of constitutive proteasome subunits with immunoproteasome subunits in the infected cell
E) The development of CD8 T cells in the thymus by inhibiting the thymoproteasome
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q3: Three major cell types, dendritic cells, macrophages,
Q4: The experiment shown in Figure uses two
Q5: The MARCH-1 E3-ubiquitin ligase is expressed in
Q6: In a mixed lymphocyte reaction, T cells
Q7: The mechanism of cross-presentation by dendritic cells
Q9: The virus shown in the diagram below
Q10: Some viruses have mechanisms to down-regulate MHC
Q11: The adaptive immune system uses multiple strategies
Q12: The invariant chain protein, Ii, has only
Q13: MHC polymorphism at individual MHC genes appears
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents