Macroeconomists who study the determinants of per capita income (the "wealth of nations")have been particularly interested in finding evidence on conditional convergence in the countries of the world.Finding such a result would imply that all countries would end up with the same per capita income once other variables such as saving and population growth rates,education,government policies,etc. ,took on the same value.Unconditional convergence,on the other hand,does not control for these additional variables.
(a)The results of the regression for 104 countries was as follows, 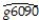 = 0.019 - 0.0006 × RelProd60,R2= 0.00007,SER = 0.016
= 0.019 - 0.0006 × RelProd60,R2= 0.00007,SER = 0.016
(0.004)(0.0073),
where g6090 is the average annual growth rate of GDP per worker for the 1960-1990 sample period,and RelProd60 is GDP per worker relative to the United States in 1960.
For the 24 OECD countries in the sample,the output is 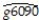 = 0.048 - 0.0404 RelProd60,R2 = 0.82,SER = 0.0046
= 0.048 - 0.0404 RelProd60,R2 = 0.82,SER = 0.0046
(0.004)(0.0063)
Interpret the results and point out the difference with regard to unconditional convergence.
(b)The "beta-convergence" regressions in (a)are of the following type, 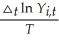 = β0 + β0 ln Yi,0 + ui,t,
= β0 + β0 ln Yi,0 + ui,t,
where △t ln Yi,t = ln Yi,0 - ln Yi,0,and t and o refer to two time periods,i is the i-th country.
Explain why a significantly negative slope implies convergence (hence the name).
(c)The equation in (b)can be rewritten without any change in information as (ignoring the division by T)
ln Yt = β0 + γ1 ln Y0 + ut
In this form,how would you test for unconditional convergence? What would be the implication for convergence if the slope coefficient were one?
(d)Let's write the equation in (c)as follows: 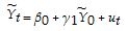 and assume that the "~" variables contain measurement errors of the following type,
and assume that the "~" variables contain measurement errors of the following type, 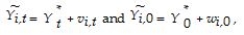 where the "*" variables represent true,or permanent,per capita income components,while v and w are temporary or transitory components.Subtraction of the initial period from the current period then results in
where the "*" variables represent true,or permanent,per capita income components,while v and w are temporary or transitory components.Subtraction of the initial period from the current period then results in 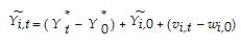 Ignoring,without loss of generality,the constant in the above equation,and making standard assumptions about the error term,one can show that by regressing current per capita income on a constant and the initial period per capita income,the slope behaves as follows:
Ignoring,without loss of generality,the constant in the above equation,and making standard assumptions about the error term,one can show that by regressing current per capita income on a constant and the initial period per capita income,the slope behaves as follows: 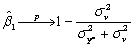 Discuss the implications for the convergence results above.
Discuss the implications for the convergence results above.
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q24: Threats to in internal validity lead to
A)perfect
Q29: Until about 10 years ago, most studies
Q30: The true causal effect might not be
Q32: A statistical analysis is internally valid if
A)all
Q32: A study of United States and Canadian
Q33: Keynes postulated that the marginal propensity to
Q34: Sir Francis Galton (1822-1911),an anthropologist and cousin
Q40: One of the most frequently used summary
Q41: Your professor wants to measure the class's
Q42: Assume that you had found correlation of
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents