One of the most frequently used summary statistics for the performance of a baseball hitter is the so-called batting average.In essence,it calculates the percentage of hits in the number of opportunities to hit (appearances "at the plate").The management of a professional team has hired you to predict next season's performance of a certain hitter who is up for a contract renegotiation after a particularly great year.To analyze the situation,you search the literature and find a study which analyzed players who had at least 50 at bats in 1998 and 1997.There were 379 such players.
(a)The reported regression line in the study is 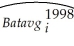 = 0.138 + 0.467 ×
= 0.138 + 0.467 × 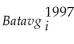 ;R2= 0.17
;R2= 0.17
and the intercept and slope are both statistically significant.What does the regression imply about the relationship between past performance and present performance? What values would the slope and intercept have to take on for the future performance to be as good as the past performance,on average?
(b)Being somewhat puzzled about the results,you call your econometrics professor and describe the results to her.She says that she is not surprised at all,since this is an example of "Galton's Fallacy." She explains that Sir Francis Galton regressed the height of offspring on the mid-height of their parents and found a positive intercept and a slope between zero and one.He referred to this result as "regression towards mediocrity." Why do you think econometricians refer to this result as a fallacy?
(c)Your professor continues by mentioning that this is an example of errors-in-variables bias.What does she mean by that in general? In this case,why would batting averages be measured with error? Are baseball statisticians sloppy?
(d)The top three performers in terms of highest batting averages in 1997 were Tony Gwynn (.372),Larry Walker (.366),and Mike Piazza (.362).Given your answers for the previous questions,what would be your predictions for the 1998 season?
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q24: Threats to in internal validity lead to
A)perfect
Q29: Until about 10 years ago, most studies
Q30: The true causal effect might not be
Q32: A study of United States and Canadian
Q37: Macroeconomists who study the determinants of per
Q41: Your professor wants to measure the class's
Q42: Assume that you had found correlation of
Q43: Assume that a simple economy could be
Q44: Your textbook states that correlation of the
Q45: Your textbook uses the following example of
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents