The fruit fly cross shown here analyzes the transmission of two genes in the X chromosome. The male parent has mutant alleles for both the white gene (w-) and the crossveinless gene (cv-) . The female parent has nonmutant forms of these genes (w+ and cw+) . A cross between siblings of the F1 generation-a red-eyed, crossveined female and a red-eyed, crossveined male-generates F2 progeny. Examine the genotype of the F2 male progeny. Notice that the progeny fall into two groups. Refer to the figure below when answering the following question. Why are the female progeny from the F1 cross shown in the figure not used for linkage analysis? 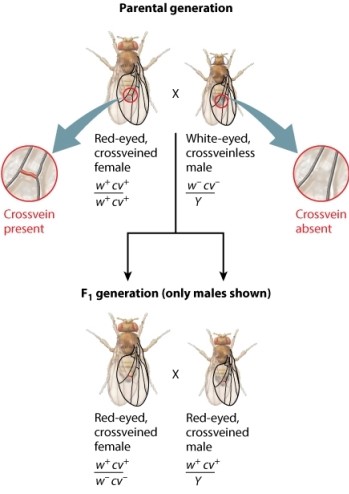
A) All F2 females exhibit the genotype associated with genes located in the X donated by the male parent from the F1 cross.
B) F2 females reveal the genotype of the F1 female parent as well as the genotype of recombinants.
C) All F2 females have a wild-type phenotype of red eyes and cross-veined wings.
D) F2 females appear to assort independently because they exhibit a 1:1:1:1 ratio.
E) F2 male progeny far outnumber the F2 female progeny.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q117: In Jabberwocks, flame eyes (F) are dominant
Q118: If a woman's husband shows an undesirable
Q119: Genes that are linked do not show:
A)dominance.
B)segregation.
C)independent
Q120: What process allows a gamete to carry
Q121: For two genes that show independent assortment,
Q123: The small area near the centromere is
Q124: During prophase I of meiosis, a physical
Q125: The ratio of recombinants to total number
Q126: The fruit fly cross shown here analyzes
Q127: The frequency of recombination is expressed as
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents