A 65-year-old woman comes to the emergency department with acute loss of vision in her right eye. Three hours ago, she was watching television when she suddenly noticed the vision in her right eye become cloudy and then go completely black. She has no headache, eye pain, double vision, dysarthria, dysphasia, muscle weakness, or numbness. Past medical history includes type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Her medications include lisinopril and metformin. She has a 40-pack-year smoking history.
Vital signs are within normal limits. Visual acuity is 20/40 in the left eye and there is no light perception in the right eye. There is a relative afferent pupillary defect on the right. Ocular motility is normal on cardinal signs of gaze testing. The remainder of the physical examination is within normal limits.
Funduscopic examination is shown in the image below.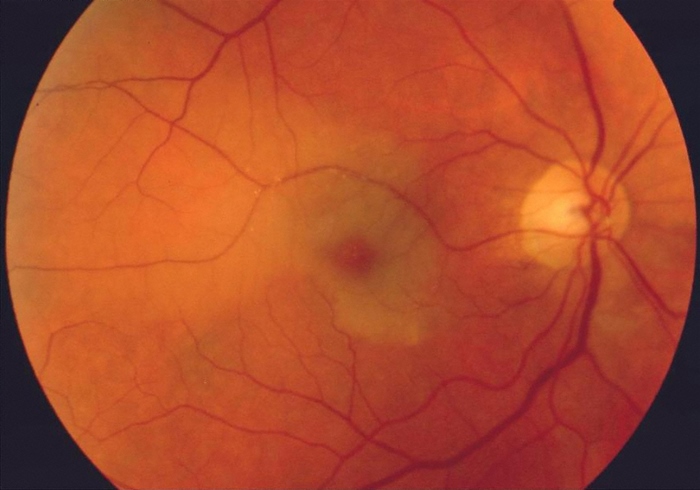
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis for this patient's acute vision loss?
A) Acute angle-closure glaucoma
B) Central retinal artery occlusion
C) Nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy
D) Optic neuritis
E) Retinal detachment
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q170: A 76-year-old man is brought to the
Q171: A 28-year-old woman is brought to the
Q172: A 72-year-old woman comes to the emergency
Q173: A 65-year-old man with a history of
Q174: A 75-year-old man with a history of
Q176: A 66-year-old woman is brought to the
Q177: A 36-year-old woman comes to the emergency
Q178: A 54-year-old man comes to the emergency
Q179: A 65-year-old woman comes to the emergency
Q180: A 54-year-old man with a history of
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents