A 23-year-old woman with a 12-year history of type 1 diabetes mellitus is hospitalized with diabetic ketoacidosis. On admission, her blood pressure is 80/60 mm Hg, pulse is 120/min, and respirations are 28/min. She weighs 60 kg (132 lb) . Her oropharynx is very dry. Abdominal examination shows diffuse tenderness without guarding or hepatosplenomegaly. The remainder of her physical examination is within normal limits.
Her clinical status improves significantly with intravenous (IV) fluids and insulin. In the first 2 hours, she receives 2 liters of isotonic saline (NS) , and this is later changed to 1/2 NS with potassium chloride (KCl) at 250 mL/hr. The patient is also receiving IV regular insulin infusion. Her blood glucose declines steadily to 188 mg/dL after 6 hours of treatment. She states that she is feeling better but still feels very nauseous.
Laboratory results are as follows: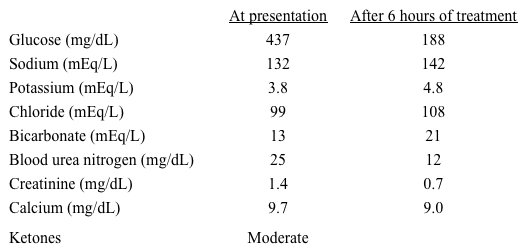
Which of the following is the most appropriate fluid management for this patient?
A) Continue 1/2 NS without KCl
B) Continue current treatment
C) Switch IV fluids to D5% 1/2 NS with KCl
D) Switch IV fluids to D5% 1/2 NS without KCl
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q31: A 24-year-old African American man complains of
Q32: A 64-year-old man hospitalized with acute myocardial
Q33: A 29-year-old woman undergoes thyroidectomy for Graves'
Q34: A 44-year-old woman is brought to the
Q35: A 79-year-old nursing home resident is admitted
Q37: An 80-year-old man is hospitalized because of
Q38: A 60-year-old man with alcoholism is admitted
Q39: An 88-year-old nursing home resident is admitted
Q40: A 66-year-old woman is admitted to the
Q41: A 63-year-old man with diabetes is hospitalized
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents