Passage
The drug paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is used to relieve pain and fever, and is a metabolite of the antipyretic drug phenacetin (Figure 1) . These two drugs have similar medicinal properties, but phenacetin has been shown to be carcinogenic and cause kidney damage. Acetaminophen is a safer alternative to phenacetin when taken in therapeutic doses.
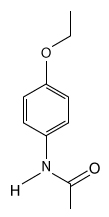 Figure 1 Structure of phenacetinA student synthesizes acetaminophen in a laboratory from phenol according to the reactions shown. The synthesis begins with the nitration of phenol by sodium nitrate (NaNO3) to produce the mixture of the isomers 2-nitrophenol and 4-nitrophenol (Reaction 1) . These isomers can be easily separated by steam distillation to isolate the desired product, 4-nitrophenol. Reduction of the nitro group with sodium borohydride (NaBH4) (Reaction 2) is followed by acetylation of the amine with acetic anhydride (Reaction 3) to afford the final product, acetaminophen.
Figure 1 Structure of phenacetinA student synthesizes acetaminophen in a laboratory from phenol according to the reactions shown. The synthesis begins with the nitration of phenol by sodium nitrate (NaNO3) to produce the mixture of the isomers 2-nitrophenol and 4-nitrophenol (Reaction 1) . These isomers can be easily separated by steam distillation to isolate the desired product, 4-nitrophenol. Reduction of the nitro group with sodium borohydride (NaBH4) (Reaction 2) is followed by acetylation of the amine with acetic anhydride (Reaction 3) to afford the final product, acetaminophen.
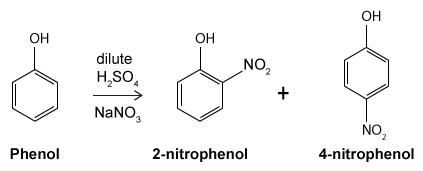 Reaction 1
Reaction 1
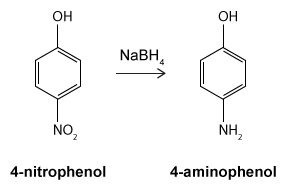 Reaction 2
Reaction 2
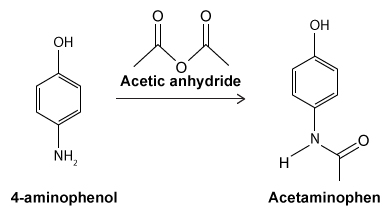 Reaction 3
Reaction 3
-Which of the following statements most accurately describes the component that remains in the reaction flask during the steam distillation?
A) 2-nitrophenol remains in the reaction flask because it has more intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
B) 4-nitrophenol remains in the reaction flask because it has more intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
C) 2-nitrophenol remains in the reaction flask because it has less intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
D) 4-nitrophenol remains in the reaction flask because it has less intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q1: Passage
A limited number of cellular functions exist
Q2: Passage
Hemophilia B is a blood clotting disorder
Q3: Passage
Hemophilia B is a blood clotting disorder
Q5: Passage
Hemophilia B is a blood clotting disorder
Q6: Passage
A limited number of cellular functions exist
Q7: Passage
The drug paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen,
Q8: Passage
Hemophilia B is a blood clotting disorder
Q9: Passage
Hemophilia B is a blood clotting disorder
Q10: Passage
The drug paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen,
Q11: Passage
A limited number of cellular functions exist
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents