Passage Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry (ESI-MS) Employs a Soft Ionization Technique
Passage
Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) employs a soft ionization technique that, unlike traditional ionization via electron bombardment, results in little to no fragmentation of target molecules. During electron bombardment, electrons collide with the analyte and cause the molecule to lose an electron whereas during ESI-MS, ions are produced by passing the analyte solution through an electrospray needle that has a potential difference applied with respect to a counterelectrode. This leads to the formation of charged droplets, which are repelled from the needle toward the counterelectrode and mass spectrometer, as shown in Figure 1.
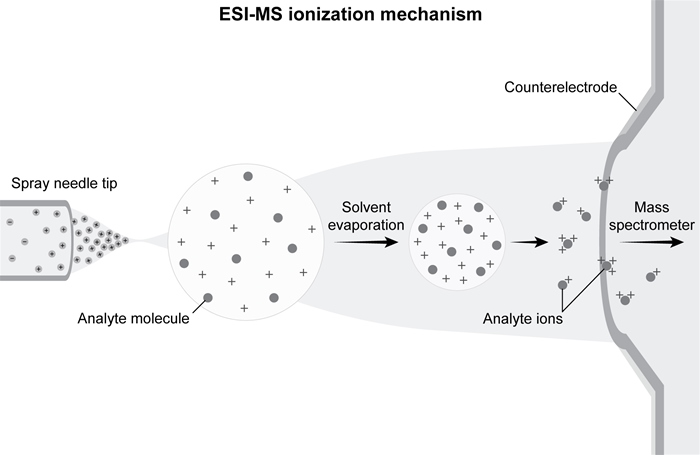 Figure 1 ESI-MS ionization mechanismDuring the droplet's flight, the solvent is evaporated off analyte molecules. Ionization occurs through the protonation of basic sites on target molecules. Reaction 1 shows the number of protons n added to molecule M.M → (M + nH) n+Reaction 1Researchers used ESI-MS to quantify the formation of four pyridyloxobutyl-DNA (POB-DNA) adducts, shown in Figure 2. POB-DNA adduct formation involves highly mutagenic pyridyloxobutylating agents, which are formed from cytochrome P450-mediated hydroxylation of 4-(methylnitrosamino) -1-(3-pyridyl) -1-butanone (NNK) , an abundant N-nitrosamine carcinogen found in cigarette smoke. Adducts were produced in vitro by treating samples of calf thymus DNA with NNK. The DNA adducts were then separated by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) and analyzed via ESI-MS.
Figure 1 ESI-MS ionization mechanismDuring the droplet's flight, the solvent is evaporated off analyte molecules. Ionization occurs through the protonation of basic sites on target molecules. Reaction 1 shows the number of protons n added to molecule M.M → (M + nH) n+Reaction 1Researchers used ESI-MS to quantify the formation of four pyridyloxobutyl-DNA (POB-DNA) adducts, shown in Figure 2. POB-DNA adduct formation involves highly mutagenic pyridyloxobutylating agents, which are formed from cytochrome P450-mediated hydroxylation of 4-(methylnitrosamino) -1-(3-pyridyl) -1-butanone (NNK) , an abundant N-nitrosamine carcinogen found in cigarette smoke. Adducts were produced in vitro by treating samples of calf thymus DNA with NNK. The DNA adducts were then separated by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) and analyzed via ESI-MS.
 Figure 2 Molecular structure of POB-DNA adducts
Figure 2 Molecular structure of POB-DNA adducts
Adapted from Lao Y, Villalta PW, Sturla SJ, Wang M, Hecht SS. Quantitation of pyridyloxobutyl DNA adducts of tobacco-specific nitrosamines in rat tissue DNA by high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. Chem Res Toxicol. 2006.
-In a second experiment, the following DNA adducts are analyzed after separation by normal-phase HPLC. Which of the following is true regarding the separation of these adducts? 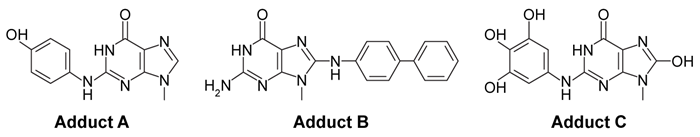
A) Adduct A has a longer retention time than Adduct C.
B) Adduct B has a longer retention time than Adduct C.
C) Adduct C elutes last.
D) Adduct B elutes last.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q94: A mixture of 1-butanol, 1-hexanol, 1-octanol, and
Q95: Passage
Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) employs a
Q96: Consider the reaction below. Q97: Which separation technique is optimal for purification Q98: Terpenes are made up of two or Q100: What is the product of the reaction Q101: Hydroxyl substituents in alcohols are poor leaving Q102: The reaction below was performed under thermodynamic Q103: Passage Q104: The amino acids Val, Leu, and Ile![]()
Students used three classification tests to study
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents