Passage
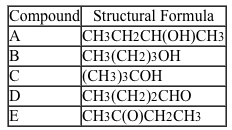
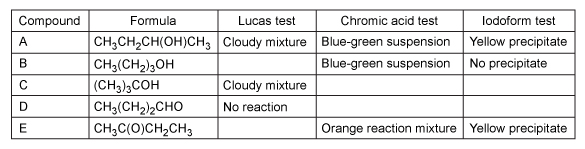
Students used three classification tests to study the reactivity of alcohol, aldehyde, and ketone functional groups in organic compounds. The organic compounds provided to the students are given in Table 1.Table 1 Organic Compounds Tested
 First, the students performed the Lucas test by mixing a few drops of each compound with 2 mL of the Lucas reagent (ZnCl2 and HCl) . This reagent is used to test for secondary and tertiary alcohols. A positive test result is indicated by a cloudy reaction mixture upon addition of the Lucas reagent due to the formation of an insoluble compound by an SN1 reaction with a secondary or tertiary alcohol (Reaction 1) .
First, the students performed the Lucas test by mixing a few drops of each compound with 2 mL of the Lucas reagent (ZnCl2 and HCl) . This reagent is used to test for secondary and tertiary alcohols. A positive test result is indicated by a cloudy reaction mixture upon addition of the Lucas reagent due to the formation of an insoluble compound by an SN1 reaction with a secondary or tertiary alcohol (Reaction 1) .
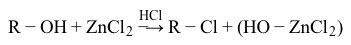 Reaction 1Next, a test for alcohols and aldehydes was performed by the addition of a drop of chromic acid reagent (CrO3 dissolved in aqueous H2SO4) into samples of the organic compounds. The disappearance of the orange color from chromic acid and formation of a blue-green suspension is indicative of a positive result for this test. Compound A was found to be an example of a positive result, as shown in Reaction 2.
Reaction 1Next, a test for alcohols and aldehydes was performed by the addition of a drop of chromic acid reagent (CrO3 dissolved in aqueous H2SO4) into samples of the organic compounds. The disappearance of the orange color from chromic acid and formation of a blue-green suspension is indicative of a positive result for this test. Compound A was found to be an example of a positive result, as shown in Reaction 2.
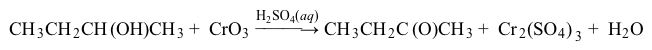 Reaction 2Finally, samples of the compounds were also dissolved in water, followed by the addition of NaOH and iodine. This test is known as the iodoform test, which is used to identify methyl ketones and secondary alcohols. A positive result is indicated by the formation of iodoform (CHI3) , a yellow precipitate (Reaction 3) .
Reaction 2Finally, samples of the compounds were also dissolved in water, followed by the addition of NaOH and iodine. This test is known as the iodoform test, which is used to identify methyl ketones and secondary alcohols. A positive result is indicated by the formation of iodoform (CHI3) , a yellow precipitate (Reaction 3) .
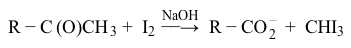 3Table 2 Selected Observations from the Classification Tests
3Table 2 Selected Observations from the Classification Tests
-Compound E does not give a positive result for the Lucas test. However, after reaction with LiAlH4, a positive result for the Lucas test is observed. Which compound is the product of the reaction of Compound E with LiAlH4?
A) Butanal
B) 1-Butanol
C) 2-Butanol
D) 2-Butanone
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q109: Compound 1 shown below is converted to
Q110: Compound 1 and PBr3 react to form
Q111: The number of different stereoisomers that exist
Q112: Q113: Passage Q115: Passage Q116: Compound 1 is shown below. Q117: If Staphylococcus aureus V8 protease is specific Q118: Passage Q119: The enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase catalyzes the conversion![]()
Students used three classification tests to study
Students used three classification tests to study
Students used three classification tests to study
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents