An 85-year-old nursing home resident is brought to the emergency department due to worsening cough, difficulty breathing, and decreased responsiveness for 3 days. Medical conditions include hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and dementia. Following evaluation that reveals leukocytosis and lung infiltrates, the patient's respiratory distress progressively worsens. Endotracheal intubation is performed; mechanical ventilation is begun; the patient is given intravenous fluids and antibiotics; a central venous catheter is placed; and she is admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) .
In the ICU, the patient requires increasing ventilatory support with elevated airway pressures. Temperature is 35.6 C (96 F) , blood pressure is 84/40 mm Hg, pulse is 112/min, and respirations are 16/min. Pulse oximetry shows 92% on assist-control mode with a tidal volume of 300 mL, fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) of 60%, and positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) of 5 cm H2O. Examination reveals decreased breath sounds on the right, rhonchi on the left, and normal S1 and S2. The abdomen is soft and nontender. There is no extremity edema.
Arterial blood gases and chest x-ray are shown below.
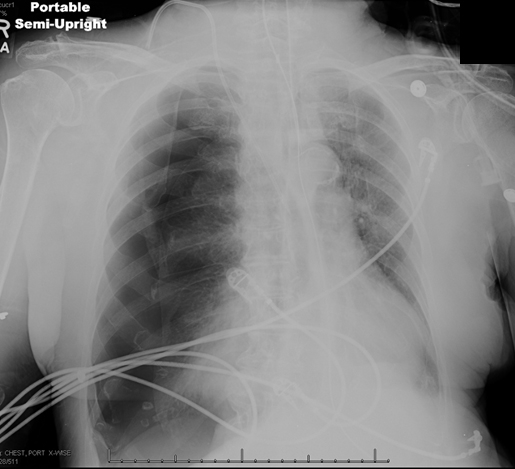
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
A) Increase the PEEP
B) Insert chest tube
C) Provide short-term neuromuscular paralysis
D) Reposition the endotracheal tube
E) Suction respiratory secretions
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q176: A 66-year-old woman is brought to the
Q177: A 36-year-old woman comes to the emergency
Q178: A 54-year-old man comes to the emergency
Q179: A 65-year-old woman comes to the emergency
Q180: A 54-year-old man with a history of
Q182: A 72-year-old man with metastatic prostate cancer
Q183: A 67-year-old man with chronic obstructive pulmonary
Q184: A 75-year-old man with moderate chronic obstructive
Q185: A 67-year-old woman comes to the emergency
Q186: A 62-year-old woman comes to the emergency
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents