Passage
The highly addictive nature of cigarettes can be partly explained by how nicotine, the primary addictive ingredient, is administered. The fastest route of administration for most drugs is through inhalation; cigarette smoking results in the transmission of nicotine to the brain in about 15 seconds. In the brain, nicotine activates the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, which stimulate the brain's reward pathway and produce mild feelings of euphoria. Those who quit smoking often relapse due to stress, weight gain, and withdrawal symptoms such as cravings and irritability. Of those who attempt to quit without formal treatment, only 3%-5% remain abstinent after a year.Research suggests that mindfulness meditation-based programs can be an effective strategy to quit smoking. Mindfulness is an aspect of meditation that involves cultivating a nonjudgmental awareness of the thoughts, emotions, and sensations arising in the present moment.For one study, researchers randomly assigned 88 smokers to either Mindfulness Training (MT) or the Freedom From Smoking (FFS) intervention developed by the American Lung Association. Both groups participated in 90-minute group training sessions twice a week for four weeks. The FFS intervention educated participants on the negative health consequences of smoking, coping strategies for cravings, and the development of healthy lifestyle habits. The MT intervention taught mindfulness meditation techniques as a way of gaining awareness and acceptance of the cognitive, emotional, and physical components of cravings. The number of cigarettes smoked per day and self-reported abstinence, as verified by exhaled carbon monoxide, were measured at the end of treatment and at a 17-week follow-up for participants in each group (Figure 1) .
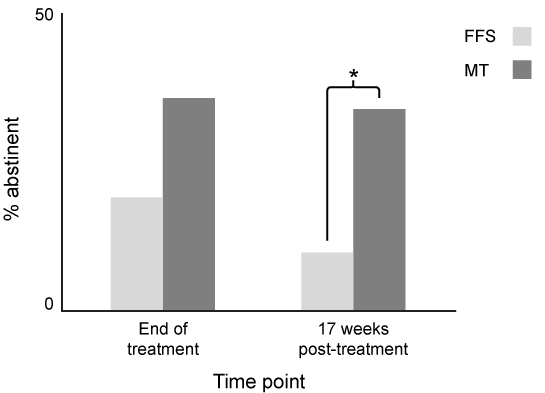 Figure 1 Percentage of participants in each group abstinent at the end of treatment and at 17-week follow-up (* indicates p < 0.05)
Figure 1 Percentage of participants in each group abstinent at the end of treatment and at 17-week follow-up (* indicates p < 0.05)
-Which of the following may be involved with physical drug dependence?Neurochemical changes in the brainWithdrawal symptoms with cessation of drug useTolerance to the drug used
A) I and II only
B) I and III only
C) II and III only
D) I, II, and III
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q53: Passage
The highly addictive nature of cigarettes can
Q54: Passage
The highly addictive nature of cigarettes can
Q55: Passage
The highly addictive nature of cigarettes can
Q56: Passage
Across the lifespan, mental and physical health
Q57: Passage
Before memories have been consolidated they are
Q59: Passage
The highly addictive nature of cigarettes can
Q60: Passage
Before memories have been consolidated they are
Q61: Passage
A common misconception in medicine is that
Q62: Passage
Visual perception involves the organization and interpretation
Q63: Passage
Major depression is a mood disorder that
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents