Passage
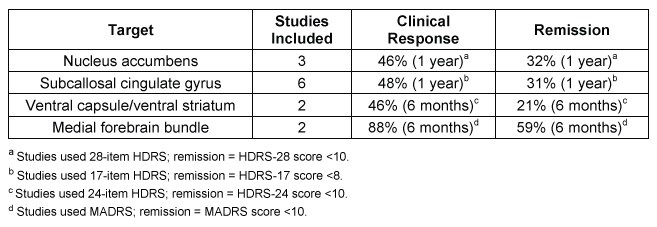
Major depression is a mood disorder that affects nearly 7% of the American population and is the most common cause of disability worldwide. Standard treatment typically involves antidepressant medication alone, although a combination of antidepressant medication and psychological treatment, such as psychotherapy or cognitive-behavioral therapy, is often more effective. However, because depression has genetic, environmental, and psychological contributing factors, treatment can be challenging. Approximately 10% of those suffering from depression have treatment-resistant depression (TRD) that does not respond to standard treatment.A number of treatment options for those with TRD target the functioning of the nervous system. Deep-brain stimulation (DBS) , which is used to treat Parkinson disease, has also been investigated as a treatment for TRD. DBS involves implanting a device in the brain that sends electrical impulses to a specific area. Although the mechanism by which DBS alleviates depressive symptoms is unclear, neurostimulation provided by DBS is thought to disrupt dysfunctional patterns of electrical activity in local areas and connected brain regions.A meta-analysis reviewed the data from several studies that used different brain regions as DBS targets in the treatment of TRD. Table 1 shows the percentage of TRD patients who underwent DBS and showed clinical responsiveness and remission of depression. Clinical response was defined as a 50% reduction in scores on a measure of depression. Various scales were used in the studies, including different versions of the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS) and Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS) . Remission of depression was defined as a score that fell below a predetermined threshold.Table 1 Percentage of TRD Patients Who Showed Clinical Response and Remission With DBS Treatment
-Which of the following is true regarding two classes of drugs commonly used to treat depression, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) ?
A) Both classes of drugs stimulate the release of serotonin into the synaptic cleft.
B) SSRIs block uptake of serotonin into the post-synaptic neuron.
C) MAOIs decrease the breakdown of serotonin within the pre-synaptic neuron.
D) MAOIs promote uptake of serotonin into the pre-synaptic neuron.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q59: Passage
The highly addictive nature of cigarettes can
Q60: Passage
Before memories have been consolidated they are
Q61: Passage
A common misconception in medicine is that
Q62: Passage
Visual perception involves the organization and interpretation
Q63: Passage
Major depression is a mood disorder that
Q65: Passage
A common misconception in medicine is that
Q66: Passage
Major depression is a mood disorder that
Q67: Passage
Visual perception involves the organization and interpretation
Q68: Passage
A common misconception in medicine is that
Q69: Passage
Visual perception involves the organization and interpretation
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents