Passage Physical Modifications Important for Consolidating Memory Are Particularly Apparent in in the Hippocampus
Passage
Physical modifications important for consolidating memory are particularly apparent in the hippocampus, especially a pathway called the Schaffer Collateral, which contains CA1 (cornu Ammonis) neurons that have been implicated in learning and memory. To study learning and memory in live mice, scientists use a stimulating electrode to generate brief electrical pulses on the dendrites of CA1 neurons in the Schaffer Collateral pathway and use a recording electrode to measure the excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) in the CA1 postsynaptic neurons.In Study 1, researchers used brief low-frequency stimulations (1-5 stimuli per second) to establish a baseline response in the CA1 postsynaptic neurons. Then, the same dendrites were given a high-frequency stimulation (50-100 stimuli per second) , referred to as a tetanus. The researchers discovered that the high-frequency tetanus induced an increase in the response in postsynaptic CA1 neurons that was long-lasting. For the control, the researchers established a baseline in a second set of CA1 neurons in the same region but did not give a high-frequency tetanus (Figure 1) .
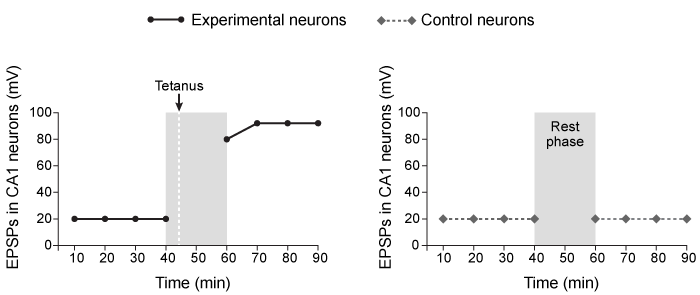 Figure 1 CA1 neuron response after a brief tetanus (experimental) or no tetanus (control) In a second behavioral study, mice were housed in either a standard cage (control) or a cage with an enhanced learning environment, including toys and access to a running wheel (experimental condition) . For the first 12 days, both groups of mice received injections of a dye that is incorporated into newly synthesized DNA, thereby providing a biomarker of neurogenesis.Following 30 days in their respective environments, all mice were tested each day for one week in the Morris Water Maze, a test that measures spatial learning and memory consolidation. Results showed that mice in the experimental condition demonstrated greater improvement on Morris Water Maze performance compared to controls. When hippocampi were examined, the results revealed that mice in the experimental condition had a greater number of dye-labeled cells than did the controls.
Figure 1 CA1 neuron response after a brief tetanus (experimental) or no tetanus (control) In a second behavioral study, mice were housed in either a standard cage (control) or a cage with an enhanced learning environment, including toys and access to a running wheel (experimental condition) . For the first 12 days, both groups of mice received injections of a dye that is incorporated into newly synthesized DNA, thereby providing a biomarker of neurogenesis.Following 30 days in their respective environments, all mice were tested each day for one week in the Morris Water Maze, a test that measures spatial learning and memory consolidation. Results showed that mice in the experimental condition demonstrated greater improvement on Morris Water Maze performance compared to controls. When hippocampi were examined, the results revealed that mice in the experimental condition had a greater number of dye-labeled cells than did the controls.
W. C. Abraham, B. Logan, J. M. Greenwood, and M. Dragunow ©2002 The Society of Neuroscience, and H. van Praag, B. R. Christie, T. J. Sejnowski, and F. H. Gage ©1999 National Academy of Sciences.
-Which of the following correctly pairs a brain area vital for learning in the Morris Water Maze with its appropriate function?
A) Cerebellum; motor learning
B) Frontal lobe; motor coordination
C) Occipital lobe; spatial processing
D) Hypothalamus; sensory relay
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q161: Passage
Text messaging while driving increases the risk
Q162: Passage
Text messaging while driving increases the risk
Q163: Passage
During the 19th century, the industrial revolution
Q164: Passage
Although the terms sex, sex category, and
Q165: Passage
Text messaging while driving increases the risk
Q167: Passage
During the 19th century, the industrial revolution
Q168: Passage
Text messaging while driving increases the risk
Q169: Passage
Although the terms sex, sex category, and
Q170: Passage
Although the terms sex, sex category, and
Q171: Passage
During the 19th century, the industrial revolution
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents