Passage Presynaptic Nerve Terminals Release Neurotransmitters Via Synaptic Vesicle Exocytosis. This
Passage
Presynaptic nerve terminals release neurotransmitters via synaptic vesicle exocytosis. This action is mediated by the membrane-bound target-SNARE (t-SNARE) proteins syntaxin and SNAP-25, and the vesicle-associated SNARE (v-SNARE) protein synaptobrevin. Membrane fusion is initiated when the t-SNAREs and v-SNAREs form an α-helix bundle known as the core-trans-complex, achieved by zipping SNARE proteins together to form a more stable cis-complex (Figure 1) .
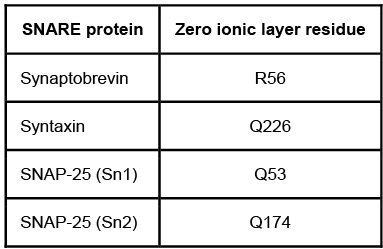
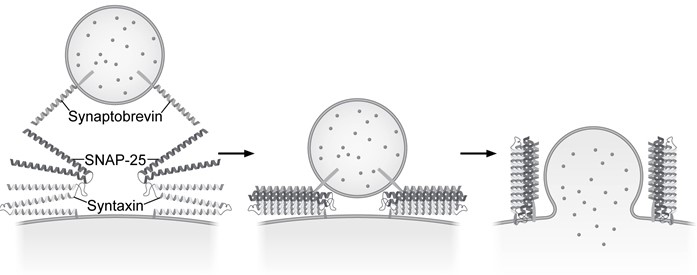 Figure 1 Formation of the core-trans-complex and subsequent membrane fusionThe cis-complex contains the zero ionic layer, the main site of interaction between complexed proteins. Within the zero ionic layer, arginine on synaptobrevin coordinates with carbonyl groups present on the other residues shown in Table 1. The zero ionic layer is buried within leucine zipper domains, which act as a shield to solvent molecules.Table 1 Composition of cis-Complex Zero Ionic Layer
Figure 1 Formation of the core-trans-complex and subsequent membrane fusionThe cis-complex contains the zero ionic layer, the main site of interaction between complexed proteins. Within the zero ionic layer, arginine on synaptobrevin coordinates with carbonyl groups present on the other residues shown in Table 1. The zero ionic layer is buried within leucine zipper domains, which act as a shield to solvent molecules.Table 1 Composition of cis-Complex Zero Ionic Layer
 An early step in cis-complex disassembly is destabilization by the ATPase N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor (NSF) , which initiates unzipping by breaking flanking leucine zipper regions, leading to vesicle reuptake. Movement of NSF to the cell membrane is mediated by the cytoplasmic protein α-SNAP, which must first bind the N-terminal domain of syntaxin.To determine the effect of vesicle-bound synaptobrevin on the binding of α-SNAP to syntaxin, increasing amounts of recombinant His-tagged α-SNAP were added to a constant amount of syntaxin affixed to glutathione-agarose beads with or without synaptobrevin. After incubation, bound proteins were recovered and quantitatively analyzed by immunoblotting. Results are shown in Figure 2.
An early step in cis-complex disassembly is destabilization by the ATPase N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor (NSF) , which initiates unzipping by breaking flanking leucine zipper regions, leading to vesicle reuptake. Movement of NSF to the cell membrane is mediated by the cytoplasmic protein α-SNAP, which must first bind the N-terminal domain of syntaxin.To determine the effect of vesicle-bound synaptobrevin on the binding of α-SNAP to syntaxin, increasing amounts of recombinant His-tagged α-SNAP were added to a constant amount of syntaxin affixed to glutathione-agarose beads with or without synaptobrevin. After incubation, bound proteins were recovered and quantitatively analyzed by immunoblotting. Results are shown in Figure 2.
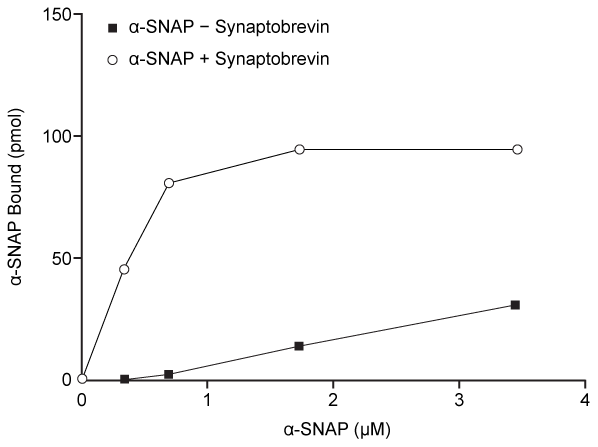 Figure 2 α-SNAP binding to syntaxin in the absence (square) or presence (circle) of synaptobrevin
Figure 2 α-SNAP binding to syntaxin in the absence (square) or presence (circle) of synaptobrevin
Adapted from Mcmahon HT, Südhof TC. Synaptic core complex of synaptobrevin, syntaxin, and SNAP25 forms high affinity alpha-SNAP binding site. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(5) :2213-7.
-Wild-type syntaxin (Synt-WT) and mutant syntaxins containing a deletion of the N-terminal sequence (SyntΔA) or C-terminal sequence (SyntΔB) were separated and incubated with α-SNAP. After washing away unbound molecules, which of the following is the most likely result of protein immunoblotting for α-SNAP?
A) 
B) 
C) 
D) 
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q12: Passage
Leptin signaling is vital for maintaining adequate
Q13: Passage
Tumor hypoxia is a marker of resistance
Q14: Passage
The innate immune system relies heavily on
Q15: Passage
Tumor hypoxia is a marker of resistance
Q16: Passage
The innate immune system relies heavily on
Q18: Passage
Presynaptic nerve terminals release neurotransmitters via synaptic
Q19: Passage
The innate immune system relies heavily on
Q20: Passage
Presynaptic nerve terminals release neurotransmitters via synaptic
Q21: Passage
The bacterium Clostridium difficile secretes protein toxins
Q22: Passage
Spinocerebellar ataxia 3 (SCA3) is a neurodegenerative
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents