Passage
The innate immune system relies heavily on the phagocytic action of neutrophils, mobile white blood cells that engulf and degrade bacteria and viruses as the first line of host defense against invading pathogens. One mechanism for eliminating viruses engulfed in the phagosome involves the degradation of viral proteins by neutrophil serine proteases (NSPs) .NSPs, which form part of the chymotrypsin family of serine proteases, cleave viral proteins using a catalytic triad relay system. Originally discovered in granules released by neutrophils, NSP4 is a novel monomeric serine protease that has been studied to elucidate the catalytic mechanism of NSPs. Prior experimental data suggest that NSP4 alters its tertiary structure upon substrate binding and cleaves viral proteins using the acylation reaction shown in Figure 1.
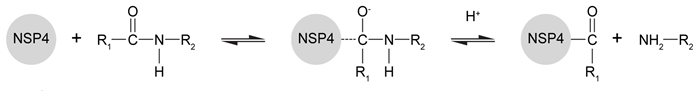 Figure 1 Degradation of viral proteins by acylation of NSP4Computational methods were used to identify the energetic parameters of reactions between NSP4 and synthetic viral proteins. To ensure that simulated reactions resembled physiological conditions, algorithms were adjusted to account for the enzyme being in an aqueous environment. The rate-determining step in the acylation reaction was determined by calculating the changes in free energy in both the enzyme and substrate (Figure 2) .
Figure 1 Degradation of viral proteins by acylation of NSP4Computational methods were used to identify the energetic parameters of reactions between NSP4 and synthetic viral proteins. To ensure that simulated reactions resembled physiological conditions, algorithms were adjusted to account for the enzyme being in an aqueous environment. The rate-determining step in the acylation reaction was determined by calculating the changes in free energy in both the enzyme and substrate (Figure 2) .
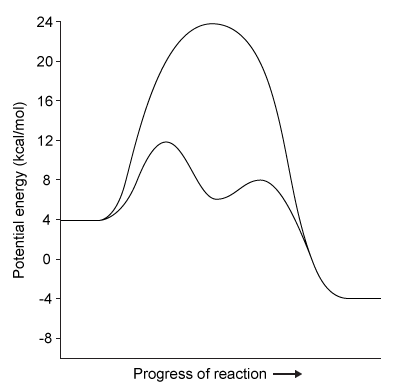 Figure 2 Free energy profiles of synthetic viral protein cleavageKnowledge of amino acid frequency distribution at an enzymatic active site may facilitate the design of novel active sites and enzyme-specific inhibitors. Researchers analyzed the composition of amino acids that form the NSP4 active site during protein folding to study the characteristics of residues involved in active site formation (Figure 3) .
Figure 2 Free energy profiles of synthetic viral protein cleavageKnowledge of amino acid frequency distribution at an enzymatic active site may facilitate the design of novel active sites and enzyme-specific inhibitors. Researchers analyzed the composition of amino acids that form the NSP4 active site during protein folding to study the characteristics of residues involved in active site formation (Figure 3) .
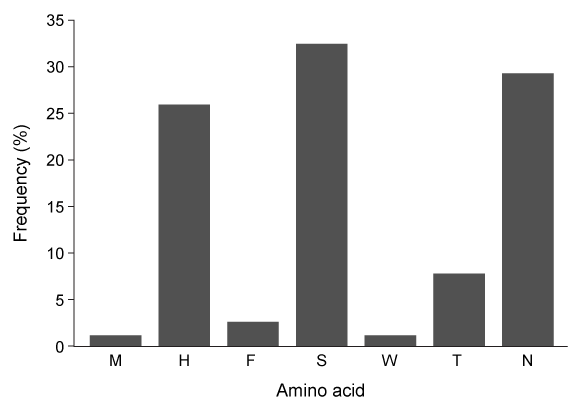 Figure 3 Frequency distribution of amino acid residues at the NSP4 active site
Figure 3 Frequency distribution of amino acid residues at the NSP4 active site
Adapted from Stapels DA, Geisbrecht BV, Rooijakkers SH. Neutrophil serine proteases in antibacterial defense. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2015;23:42-8.
-Which of the following is the most accurate statement regarding NSP4 binding of viral proteins?
A) NSP4 undergoes an energy-requiring conformational change upon binding.
B) NSP4 quaternary structure must undergo conformational changes upon binding.
C) Heat is consumed when NSP4 binds its substrate.
D) A NSP4 holoenzyme is formed after the release of products.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q14: Passage
The innate immune system relies heavily on
Q15: Passage
Tumor hypoxia is a marker of resistance
Q16: Passage
The innate immune system relies heavily on
Q17: Passage
Presynaptic nerve terminals release neurotransmitters via synaptic
Q18: Passage
Presynaptic nerve terminals release neurotransmitters via synaptic
Q20: Passage
Presynaptic nerve terminals release neurotransmitters via synaptic
Q21: Passage
The bacterium Clostridium difficile secretes protein toxins
Q22: Passage
Spinocerebellar ataxia 3 (SCA3) is a neurodegenerative
Q23: Passage
Spinocerebellar ataxia 3 (SCA3) is a neurodegenerative
Q24: Passage
The liver plays a central role in
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents