Passage
Spinocerebellar ataxia 3 (SCA3) is a neurodegenerative disease that manifests as a progressive decrease in coordination of limbs and frequently results in impaired speech and eye coordination. It is associated with extension of the polyglutamine (polyQ) region of the ataxin-3 protein. The polyQ region is encoded by a series of consecutive CAG codons known as poly-CAG repeats. These regions vary in length from one person to another, ranging from as few as 10 to as many as 80 repeats. SCA3 has been reported in patients with polyQ regions exceeding ~55 repeats, and increased polyQ length correlates with earlier onset of the disease and greater clinical severity.Circular dichroism (CD) is a method of assessing protein secondary structure. It measures a molecule's ability to absorb left- and right-handed circularly polarized light of varying wavelengths. The absorption difference is known as "ellipticity," denoted by Δε. Alpha-helices have a maximum Δε at 190 nm, and beta-sheets have a maximum Δε at 200 nm.CD results show that as the length of the ataxin-3 polyQ region increases, alpha-helical nature is lost and the protein aggregates, ultimately precipitating out of solution and depositing in brain and other tissues. Furthermore, as proteins aggregate, they form beta-sheets. These beta-sheets are in the parallel orientation, and each sheet can interact with sheets in other proteins to form long, insoluble structures known as amyloid fibers (Figure 1) .
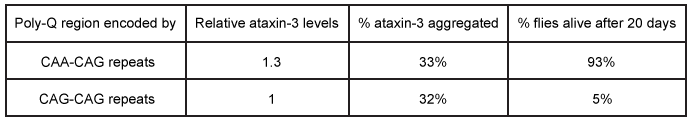
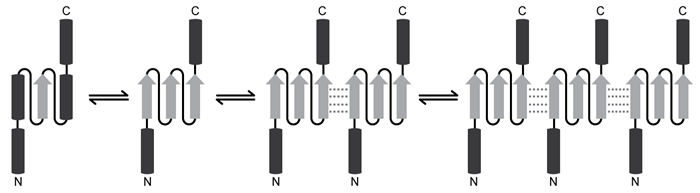 Figure 1 Depiction of the ataxin-3 polyQ region shifting from alpha-helical (cylinders) to beta-sheet (arrows) structure and aggregatingGlutamine can be encoded by both CAG and CAA codons. Researchers investigated survival rates in fruit flies expressing ataxin-3 with polyQ regions of equal length encoded by either CAG-CAG or CAA-CAG repeats (Table 1) . The protein products had identical amino acid sequences.Table 1 Fruit Fly Survival Rates Relative to Ataxin-3 Expression
Figure 1 Depiction of the ataxin-3 polyQ region shifting from alpha-helical (cylinders) to beta-sheet (arrows) structure and aggregatingGlutamine can be encoded by both CAG and CAA codons. Researchers investigated survival rates in fruit flies expressing ataxin-3 with polyQ regions of equal length encoded by either CAG-CAG or CAA-CAG repeats (Table 1) . The protein products had identical amino acid sequences.Table 1 Fruit Fly Survival Rates Relative to Ataxin-3 Expression
 Adapted from Bevivino AE, Loll PJ. An expanded glutamine repeat destabilizes native ataxin-3 structure and mediates formation of parallel beta -fibrils. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98(21) :11955-60.
Adapted from Bevivino AE, Loll PJ. An expanded glutamine repeat destabilizes native ataxin-3 structure and mediates formation of parallel beta -fibrils. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98(21) :11955-60.
-Which of the following could increase the stability of the beta-conformation of long polyglutamine regions?
A) Stacking interactions between glutamine side chains
B) Frequent beta-turns induced by glutamine flexibility
C) Rigidity of glutamine residues that induces tight turns
D) Hydrogen bonding between glutamine side chains
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q17: Passage
Presynaptic nerve terminals release neurotransmitters via synaptic
Q18: Passage
Presynaptic nerve terminals release neurotransmitters via synaptic
Q19: Passage
The innate immune system relies heavily on
Q20: Passage
Presynaptic nerve terminals release neurotransmitters via synaptic
Q21: Passage
The bacterium Clostridium difficile secretes protein toxins
Q23: Passage
Spinocerebellar ataxia 3 (SCA3) is a neurodegenerative
Q24: Passage
The liver plays a central role in
Q25: Passage
The innate immune system relies heavily on
Q26: Passage
The bacterium Clostridium difficile secretes protein toxins
Q27: Passage
The innate immune system relies heavily on
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents