Passage
Renal reabsorption of glucose is facilitated by sodium-glucose linked transporters (SGLTs) , which are secondary active transport proteins located in the apical membrane of the proximal tubular cells in the kidney. SGLT activity determines the transport maximum of glucose Tm, the maximum rate at which the kidneys can reabsorb glucose.Excretion of glucose in the urine (glycosuria) occurs when the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of glucose exceeds the Tm. Glycosuria is a symptom of diabetes mellitus, a disease marked by hyperglycemia (elevated serum glucose) . Uncontrolled hyperglycemia can damage the nerves that innervate urinary tract musculature, resulting in urinary retention (inability to fully empty the bladder) or incontinence (involuntary urine leakage) .Canagliflozin is a SGLT inhibitor used for the treatment for diabetes. The effect of canagliflozin on renal glucose reabsorption was tested in a glucose infusion experiment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) . First, researchers measured the participants' fasting serum glucose levels (average ~80 mg/dL) and then began a continuous intravenous infusion of a glucose solution. The rate of glucose infusion was adjusted such that blood glucose concentration steadily rose to 300 mg/dL. Blood and urine glucose concentrations were measured at 30-minute intervals. The experiment was later repeated in the same patients following canagliflozin administration (100 mg, once a day for seven days) . The results of both trials are shown in Figure 1.
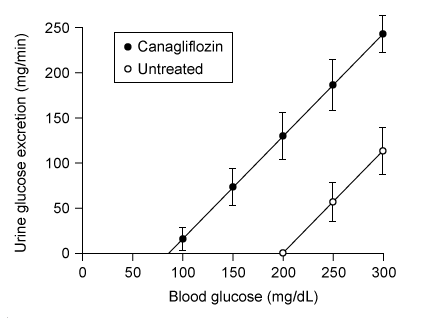 Figure 1 Mean urine glucose excretion versus blood glucose concentration in patients with T2DM, with and without canagliflozin treatmentResearchers then estimated the new Tm of glucose following canagliflozin treatment (Figure 2) . Canagliflozin was found to also lower fasting blood glucose in individuals with T2DM. Side effects included weight loss, increased urinary frequency, excessive thirst, and blood pressure reduction.
Figure 1 Mean urine glucose excretion versus blood glucose concentration in patients with T2DM, with and without canagliflozin treatmentResearchers then estimated the new Tm of glucose following canagliflozin treatment (Figure 2) . Canagliflozin was found to also lower fasting blood glucose in individuals with T2DM. Side effects included weight loss, increased urinary frequency, excessive thirst, and blood pressure reduction.
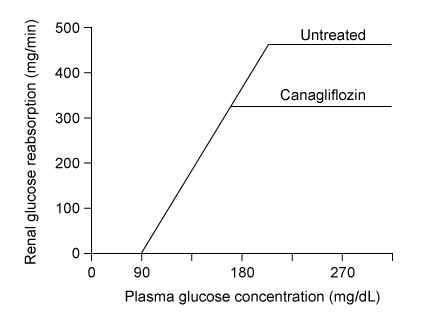 Figure 2 Mean rate of renal glucose reabsorption versus plasma glucose concentration in patients with T2DM, with and without canagliflozin treatment
Figure 2 Mean rate of renal glucose reabsorption versus plasma glucose concentration in patients with T2DM, with and without canagliflozin treatment
-Urinary retention in patients with poorly controlled diabetes mellitus is most likely the result of nerve damage impairing smooth muscle contraction in which of the following structures?
A) Bladder
B) Urethral sphincters
C) Kidney
D) Ureter
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q112: Passage
Skin grafting is a procedure in which
Q113: Passage
Obesity is a condition that affects over
Q114: Passage
Skin grafting is a procedure in which
Q115: Passage
Renal reabsorption of glucose is facilitated by
Q116: Passage
Renal reabsorption of glucose is facilitated by
Q118: Passage
In 1906, the Nobel Prize in Physiology
Q119: Passage
In 1906, the Nobel Prize in Physiology
Q120: Passage
In 1906, the Nobel Prize in Physiology
Q121: Passage
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) is an important regulator
Q122: Passage
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) is an important regulator
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents