Passage
Dmitri Mendeleev is credited with grouping the elements by atomic mass and observing that similar properties emerge periodically. Henry Moseley then determined that a fundamental property, which Ernest Rutherford later called the atomic number, is more important than atomic mass for ordering the elements.As the periodic table took shape, scientists noted certain properties and trends. For example, Rayleigh and Ramsay observed that some elements are unreactive and gave them the name noble gases. But it was not until Niels Bohr described his model of the atom that scientists understood why noble gases are stable.Another important trend was discovered by Linus Pauling. He was the first to identify electronegativity as a way to describe bonds that are neither completely ionic nor completely covalent. Pauling assigned fluorine the highest electronegativity value of 4.0 because of its strong tendency to attract electrons when bonded to other atoms. All other atoms were assigned values relative to fluorine. This became known as the Pauling electronegativity scale.Scientists identified other trends based on x-ray crystallography and reactivity studies. Figure 1 shows the first ionization energy of the elements, and Figure 2 shows electron affinity.
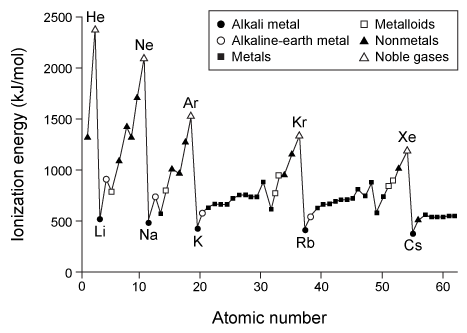 Figure 1 First ionization energy of elements
Figure 1 First ionization energy of elements
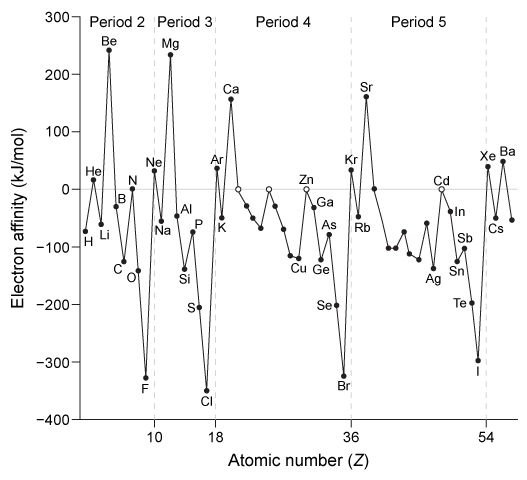 Figure 2 Electron affinity of several elements (larger negative values indicate greater electron affinity)
Figure 2 Electron affinity of several elements (larger negative values indicate greater electron affinity)
-The difference between the first and second ionization energies for magnesium is approximately 700 kJ/mol. The difference between the second and third ionization energies will likely be:
A) higher because the first and second ionization energies remove electrons from the p orbitals whereas the third removes an electron from an s orbital.
B) higher because the first and second ionization energies remove valence electrons whereas the third removes a core electron.
C) lower because the first and second ionization energies remove spin-paired electrons whereas the third removes an electron that is not spin-paired.
D) lower because the first and second ionization energies remove electrons from the n = 2 subshell whereas the third removes an electron from the n = 3 subshell.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q78: Passage
Combustion occurs when an oxidation-reduction reaction takes
Q79: Passage
Combustion occurs when an oxidation-reduction reaction takes
Q80: Passage
An automated external defibrillator (AED) is a
Q81: A radioactive atom decays by 5 alpha,
Q82: The bonds of four salts (MgBr2, NaCl,
Q84: Sebacic acid (HOOC−(CH2)8−COOH) is a naturally occurring
Q85: Ozone (O3) in the atmosphere protects against
Q86: Researchers wished to mimic the conditions of
Q87: Passage
Kidney stones are a common ailment affecting
Q88: Passage
Dmitri Mendeleev is credited with grouping the
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents