Passage
Hyperbaric oxygenation therapy involves placing a patient in a chamber with oxygen-rich air at greater than atmospheric pressure. Normal air has approximately 78% N2, 21% O2, and trace amounts of other gases. The pressure within the hyperbaric chamber is typically measured in terms of ATA, or atmospheres absolute (1 ATA is the average atmospheric pressure at sea level, or 1 atm) . A hyperbaric chamber set at 2.5 ATA would be the average atmospheric pressure at sea level (1 ATA) plus the additional pressure applied to the chamber (1.5 ATA) .There are two main types of hyperbaric chambers: monoplace chambers and multiplace chambers. Monoplace chambers accommodate a single person. The air in these chambers is 100% oxygen and can be raised to a maximum pressure of 3 ATA. Monoplace chambers are used as therapy for conditions where oxygen supply has been depleted, such as carbon monoxide poisoning. They are also used when a higher concentration of oxygen in plasma is needed, such as in wound healing.Multiplace chambers are large enough to house at least four people. The air in these chambers is typically a mixture of oxygen and nitrogen, but the patient breathes pure oxygen through a mask. Some multiplace chambers can endure maximum pressures of 6 ATA and are typically used to eliminate intravascular air bubbles that can occur from decompression sickness or embolisms. The high pressure from the multiplace chamber results in a decrease in volume of any air pockets within the body, including the sinuses, inner ear, and unwanted air bubbles in the arteries or veins.Patients report that their ears "pop" during the pressurization process, similar to being on an airplane in flight. In addition, they report that although there is an initial sense of temperature increasing, the chamber's temperature stays relatively stable during both the pressurization and the depressurization processes.
-The graph below shows how much certain real gases deviate from ideal behavior. If the ideal gas law is considered to give a close approximation for the behavior of a real gas that has a deviation of 1.0% or less, based on the graph, which of the following statements is true? 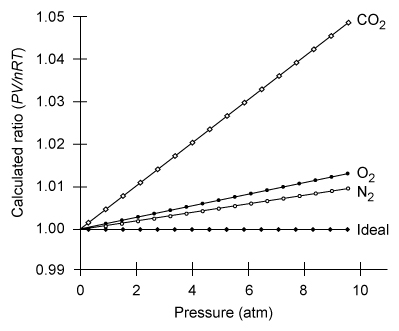
A) At pressures between 2.0 and 4.0 atm, the ideal gas law gives a close approximation for the behavior of O2 and N2, but does not give a close approximation for the behavior of CO2.
B) At atmospheric pressure, the ideal gas law gives a close approximation for the behavior of CO2 but does not give a close approximation for the behavior of O2 and N2.
C) At pressures below 4.0 atm, O2 behaves more like an ideal gas than both N2 and CO2.
D) At pressures above 4.0 atm, the ideal gas law gives a close approximation for the behavior of O2, N2, and CO2.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q196: Passage
Students were asked to bring items from
Q197: Passage
Students were asked to bring items from
Q198: Consider the neutralization curve of aqueous ammonia
Q199: Fructose 6-phosphate (Fru-6-P) breaks down in water
Q200: Passage
Students were asked to bring items from
Q202: Which of the following statements describe a
Q203: Passage
Copper plays a vital role as a
Q204: Passage
Copper plays a vital role as a
Q205: Passage
Hyperbaric oxygenation therapy involves placing a patient
Q206: Passage
Hyperbaric oxygenation therapy involves placing a patient
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents