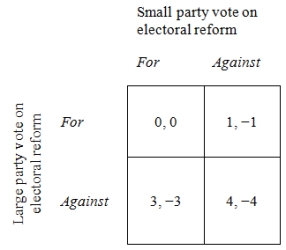
Now, let's ask what happens when the parties play a game like the one in Figure 1,
Figure 1. The Electoral Reform Game-Example 1
 except that the benefit to the large party of having disproportional rules is much less, and the penalties to the smaller party from disproportional electoral rules are lower. This might be because the smaller party has been attracting a larger electorate, whereas the large party has been losing voters. This new situation is modeled in Figure 3 below. Using Figure 3, answer the following questions.
except that the benefit to the large party of having disproportional rules is much less, and the penalties to the smaller party from disproportional electoral rules are lower. This might be because the smaller party has been attracting a larger electorate, whereas the large party has been losing voters. This new situation is modeled in Figure 3 below. Using Figure 3, answer the following questions.
Figure 3. The Electoral Reform Game-Example 2
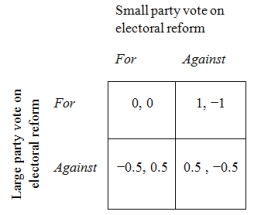
-What strategy combination(s) form(s) a Nash equilibrium in the above game? Hint: use the form (Large strategy; Small strategy) .
A) For; For
B) For; Against and Against; For
C) Against; For
D) Against; Against
E) For; Against
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q42: Answer the following questions. Q43: Answer the following questions. Q44: Answer the following questions. Q45: All electoral systems create at least some Q46: Choosing Electoral Rules: A Game-Theoretic Approach Q47: Choosing Electoral Rules: A Game-Theoretic Approach Q48: Now, suppose the large party controls which Q49: Now, suppose the large party controls which Q51: Now, let's ask what happens when the Q52: Now, let's ask what happens when the Unlock this Answer For Free Now! View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents
![]()
![]()
![]()
When would
When would

