Wild-type mice are adoptively transferred with naive CD4 T cells isolated from OT-II T-cell receptor transgenic mice. These OT-II T cells are specific for a peptide of the chicken ovalbumin protein (OVA) bound to MHC class II. After transfer, the OT-II cells rapidly disperse to all of the secondary lymphoid organs in the recipient mice. Half of the recipient mice are then given OVA protein dissolved in their drinking water, and the other half of the mice receive normal drinking water for 5 days. On the following day (day 6), lymphocytes from the spleen, the peripheral lymph nodes (LN), mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN), Peyer's patches (PP) and lamina propria (LP) are isolated and examined for the proportions of CD4 T cells in each organ expressing FoxP3. The results are shown in Figure. 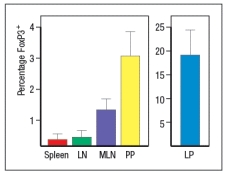
a) What is the conclusion from this experiment?
To investigate this further, dendritic cells are isolated from the spleen (spl-DC) or from the lamina propria of the small intestine (LP-DC). Each subset of dendritic cells is pulsed with the OVA protein, and then incubated with naive OT-II CD4 T cells for 5 days in the presence or absence of TGF- . The CD4 T cells are then examined for FoxP3 expression; the results are shown in Figure. 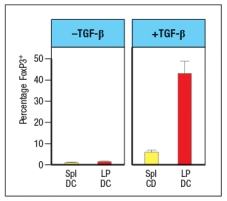
b) Why is TGF- added in this experiment?
c) What is the major difference between the splenic dendritic cells and those isolated from the lamina propria?
The CD4 T cells from the experiment above, in which the T cells were cultured for 5 days with OVA-pulsed splenic or lamina propria dendritic cells in the presence or absence of TGF- , were also assessed for their surface expression of the integrin 4 7.
d) Of the four groups of T cells shown in the graph, which ones would be expected to show high levels of 4 7?
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q17: Reovirus is an enteric virus that
Q18: In a second experiment, the isolated
Q19: Macrophages were isolated from the spleen or
Q20: Secretory IgA produced in the epithelium of
Q21: Recurrent infections with the enteric pathogen Clostridium
Q23: Oral tolerance to food antigens and immune
Q24: Like wild-type (WT) mice, Rag-deficient
Q25: IL-10-deficient mice develop spontaneous colitis, a disease
Q26: When mice are born, their intestinal lamina
Q27: IPEX syndrome is a genetic disease
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents