Following an acute virus infection in which the host clears the virus by approximately one week post-infection, a population of virus-specific memory CD8 T cells is maintained and can be detected for months to years post-infection. In mice with a knockout of a single cytokine, virus-specific memory CD8 T cells cannot be maintained, and disappear over time as shown in Figure. 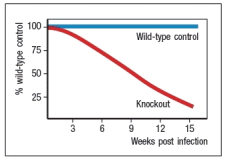
The most likely identity of the cytokine that is missing in these knockout mice is:
A) IL-15
B) IL-2
C) IL-21
D) IL-23
E) IL-4
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q18: The immune response to helminthic worm infections
Q19: Individuals with the HIV-induced immunodeficiency disease
Q20: In some infectious diseases, antibodies specific for
Q21: Hyper-IgE syndrome, also known as Job’s
Q22: Vaccinia virus, used to immunize individuals against
Q23: Studies in mice have shown that
Q24: The generation of optimal CD8 T cell
Q26: One of the first studies using peptide:MHC
Q27: Synthesis question: Leishmania parasites are intracellular
Q28: It is well documented that antibody affinities
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents