A 34-year-old woman, gravida 2 para 1, at 38 weeks gestation comes to the emergency department for contractions and vaginal spotting. The contractions started 4 hours ago and are now occurring every 3 minutes. She reports normal fetal movement and no leakage of fluid. The patient had no prenatal care but was hospitalized at 18 weeks gestation for viral gastroenteritis. A fetal ultrasound performed during this hospitalization was normal. The patient's previous delivery, a year ago, was a term cesarean delivery for breech presentation. The patient has no chronic medical conditions and has had no other surgeries. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Temperature is 36.7 C (98 F) , blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg, and pulse is 84/min. The fetal heart rate tracing is shown below: 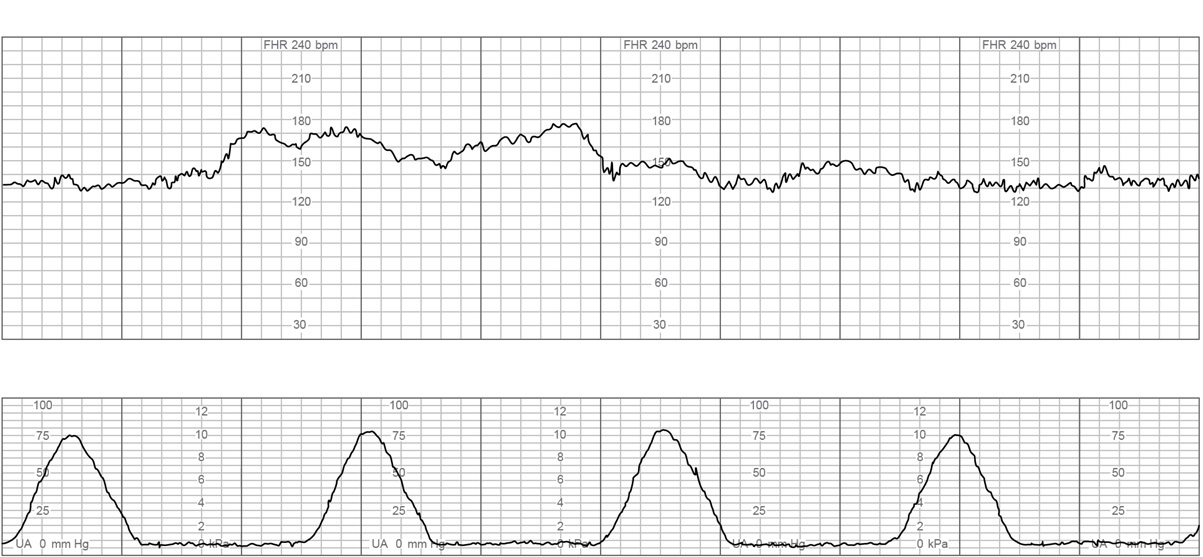 Examination shows the cervix to be 5 cm dilated and 80% effaced, with the fetal head at 0 station. Blood type is O, Rh negative. The patient is admitted and epidural anesthesia is administered. Two hours later, the patient has spontaneous rupture of membranes and becomes acutely uncomfortable. Blood pressure is 140/92 mm Hg and pulse is 100/min. The fetal heart rate tracing now is shown below:
Examination shows the cervix to be 5 cm dilated and 80% effaced, with the fetal head at 0 station. Blood type is O, Rh negative. The patient is admitted and epidural anesthesia is administered. Two hours later, the patient has spontaneous rupture of membranes and becomes acutely uncomfortable. Blood pressure is 140/92 mm Hg and pulse is 100/min. The fetal heart rate tracing now is shown below: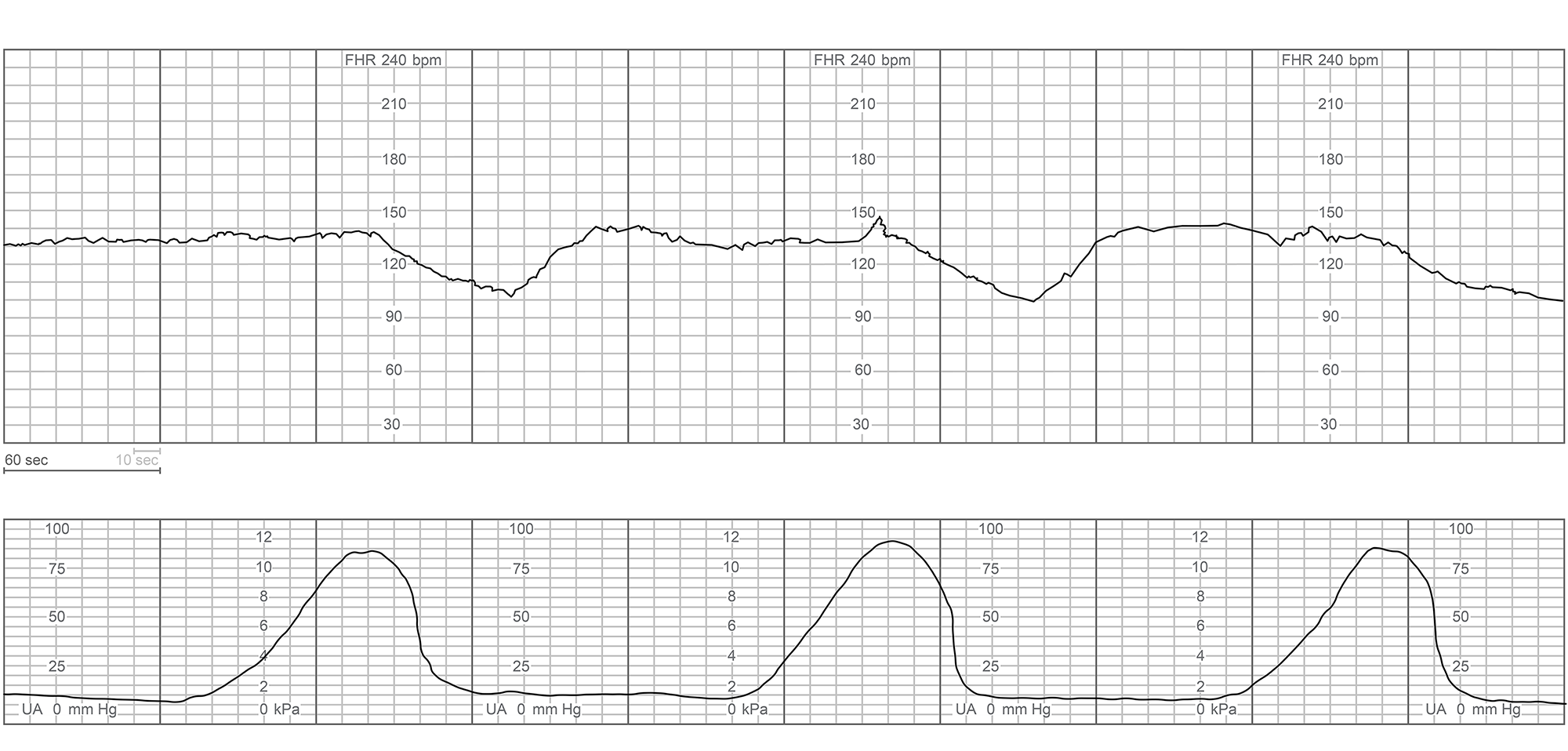 The patient begins to have heavy vaginal bleeding. The cervix is now 5 cm dilated and 80% effaced, with the fetal head at -3 station. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
The patient begins to have heavy vaginal bleeding. The cervix is now 5 cm dilated and 80% effaced, with the fetal head at -3 station. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A) Increase epidural anesthesia and start amnioinfusion
B) Perform emergency laparotomy
C) Perform emergency operative vaginal delivery
D) Place a fetal scalp electrode and continue labor
E) Start magnesium infusion and give Rho(D) immune globulin
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q773: A 22-year-old woman comes to the emergency
Q774: A 36-year-old woman, gravida 3 para 2,
Q775: A 48-year-old Hispanic woman with no past
Q776: A 3-year-old Caucasian boy is brought to
Q777: A 67-year-old man with a advanced multiple
Q779: A 27-year-old woman, gravida 3 para 1
Q780: A 23-year-old woman, gravida 3 para 2,
Q781: A 29-year-old woman, gravida 1 para 0,
Q782: A 39-year-old woman, gravida 3 para 2,
Q783: A 29-year-old woman, gravida 2 para 0
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents