Messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single RNA strand encoding a "blueprint" for an amino acid sequence (e.g. a protein, after folding and posttranslational modification) . The brief existence of an mRNA macromolecule begins with transcription and ends in enzymatic hydrolysis to ribonucleotides. Whereas mRNA is basically "ready to use" after transcription in non-eukaryotes, eukaryotic mRNA requires extensive processing. In the process called 5'cap addition, a modified 7-methylguanosine ribonucleotide is added via an unusual 5' to 5' triphosphate linkage. What is the chemical structure of the 5'-end of the mRNA strand after capping?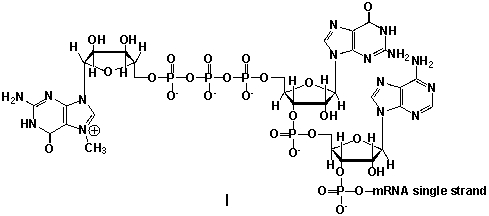
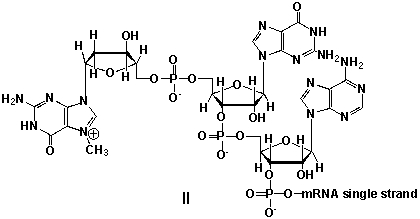
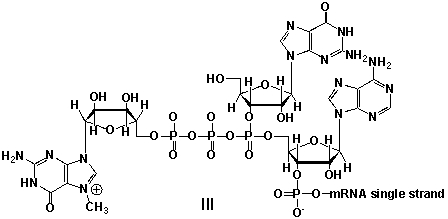
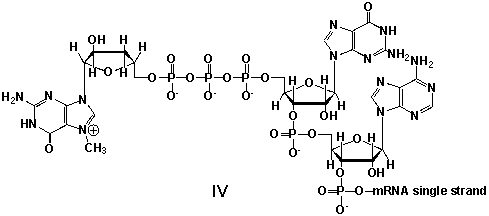
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q2: Which is the complementary tetranucleotide for 5'-AGCT-3'?
A)
Q3: Which is the DNA complement for 5'-ACCGTTAAT-3'?
A)
Q4: Which are types of RNA?
I. ribosomal
II. histonal
III.
Q5: Which statement about the base mole-percent composition
Q6: Which structure is a nucleoside? Q7: Hydrogen bonding is strongest between which two Q8: DNA-supercoiling occurs because of the following phenomena: Q9: Chlorambucil is a chemotherapeutic drug used in Q10: Dideoxynucleotides (ddNTPs, shown here is dideoxyguanosine) are Q11: What is the correct name for this![]()
I.
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents