Passage
Living organisms that require oxygen to respire can build up hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) as a byproduct of respiration. Because hydrogen peroxide can cause oxidative damage to cells, the amount of H2O2 in cells must be closely regulated. Although H2O2 decomposes spontaneously, a catalyst is needed for the reaction to occur at a sufficiently rapid rate suitable for biological purposes. In biological systems, an enzyme called a catalase accelerates the catalytic decomposition of H2O2 into water and oxygen (Reaction 1) .
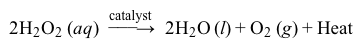 Reaction 1In a laboratory setting, several different inorganic compounds can also serve as catalysts for H2O2 decomposition, allowing researchers to compare how different catalysts affect the efficiency of the reaction. To compare Fe(NO3) 3 (a metal homogeneous catalyst) and NaI (a halogen homogeneous catalyst) , researchers measured the amount of heat evolved after placing each catalyst in a fresh solution of 3% hydrogen peroxide.To perform the measurements, the researchers placed 50 mL of 3% H2O2 in an insulated coffee cup to be used as a calorimeter, as shown in Figure 1. Before adding any catalyst, the initial, baseline temperature of the H2O2 solution was determined by recording the temperature every 30 seconds for 5 minutes. Then 10 mL of 0.10 M Fe(NO3) 3(aq) catalyst was added to the H2O2 solution. The temperature was recorded every 30 seconds for another 15 minutes. The experiment was then repeated using 10 mL of 0.50 M sodium iodide in 0.01 M NaOH as the catalyst. The results for each reaction are shown in Figure 2.
Reaction 1In a laboratory setting, several different inorganic compounds can also serve as catalysts for H2O2 decomposition, allowing researchers to compare how different catalysts affect the efficiency of the reaction. To compare Fe(NO3) 3 (a metal homogeneous catalyst) and NaI (a halogen homogeneous catalyst) , researchers measured the amount of heat evolved after placing each catalyst in a fresh solution of 3% hydrogen peroxide.To perform the measurements, the researchers placed 50 mL of 3% H2O2 in an insulated coffee cup to be used as a calorimeter, as shown in Figure 1. Before adding any catalyst, the initial, baseline temperature of the H2O2 solution was determined by recording the temperature every 30 seconds for 5 minutes. Then 10 mL of 0.10 M Fe(NO3) 3(aq) catalyst was added to the H2O2 solution. The temperature was recorded every 30 seconds for another 15 minutes. The experiment was then repeated using 10 mL of 0.50 M sodium iodide in 0.01 M NaOH as the catalyst. The results for each reaction are shown in Figure 2.
 Figure 1 Coffee cup calorimeter
Figure 1 Coffee cup calorimeter
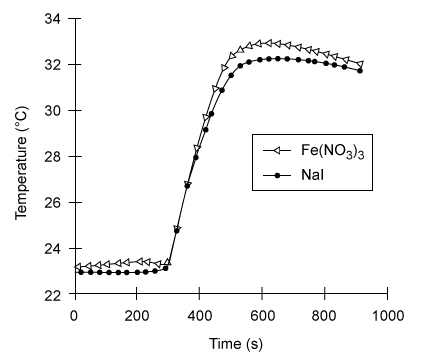 Figure 2 Temperature vs. time measurements for reactions catalyzed by Fe(NO3) 3 and NaI
Figure 2 Temperature vs. time measurements for reactions catalyzed by Fe(NO3) 3 and NaI
Adapted from: C. Marzzacco, "The effect of a change in catalyst on the enthalpy of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide." Chem13 News Magazine. ©2008 University of Waterloo.
-How is the activation energy for the decomposition of H2O2 affected by the addition of NaI to the coffee cup?
A) Increased, because adding NaI changes the concentration of the reactants in the reaction vessel
B) Increased, because NaI lowers the bond dissociation energy of H2O2
C) Decreased, because NaI stabilizes the transition state of the reaction
D) Decreased, because NaI increases the amount of heat produced from the reaction
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q232: When comparing single, double, and triple covalent
Q233: The conjugate acid of the dihydrogen orthosilicate
Q234: Passage
Within the renal system, two buffers operate
Q235: The emission line spectrum of hydrogen displays
Q236: Passage
Amino acids and copper both serve vital
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents