A 38-year-old man admitted with severe, acute alcoholic pancreatitis is evaluated in the intensive care unit for persistent fever. The patient is intubated and on mechanical ventilation. He is receiving nasojejunal tube feeding and intravenous crystalloids.
His temperature is 38.3 C (101 F) , blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg, pulse is 104/min, and respirations are 18/min. Respiratory secretions are scant. Breath sounds are decreased at the lung bases. There is epigastric tenderness on deep palpation and mild abdominal distension. 2+ presacral edema is present. A peripherally inserted central catheter in the right arm shows no surrounding skin redness or discharge.
Laboratory results are as follows: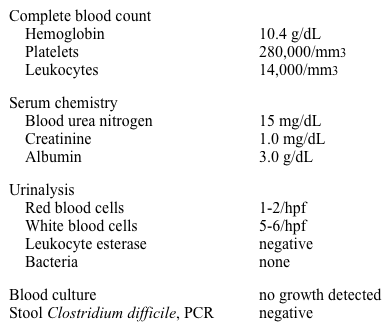
Chest x-ray reveals bilateral, small pleural effusions. A contrast-enhanced abdominal CT scan reveals 40% pancreatic necrosis and moderate-size fluid collections in the retroperitoneum around the pancreas. The gallbladder has some sludge, the common bile duct measures 5 mm, and no intrahepatic ductal dilation is seen.
Which of the following is the best next step in managing this patient?
A) Ceftriaxone and vancomycin
B) Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
C) Open necrosectomy
D) Parenteral nutrition
E) Percutaneous CT-guided aspiration
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q17: A 26-year-old primigravid woman at 36 weeks
Q18: A 75-year-old man comes to the emergency
Q19: A 52-year-old woman is undergoing screening colonoscopy
Q20: An 84-year-old man comes to the emergency
Q21: A 52-year-old man comes to the physician
Q23: A 56-year-old man comes to the emergency
Q24: A 48-year-old woman is admitted to the
Q25: A 22-year-old woman is brought to the
Q26: A 55-year-old man with known hepatic cirrhosis
Q27: A 30-year-old woman with ulcerative colitis treated
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents