A 62-year-old hospitalized man is evaluated for new-onset, right lower extremity pain. The patient underwent bypass surgery for 3-vessel coronary artery disease 2 months ago. He arrived at the emergency department 2 nights ago due to recurrent chest pains. At that time, ECG showed sinus rhythm with no ST-segment changes, but cardiac troponin I levels were elevated. The patient was initiated on unfractionated heparin, antiplatelet agents, a beta blocker, and a nitrate. A coronary angiogram was performed via the radial artery; it revealed graft insertion site stenosis and was treated with stenting. Postintervention echocardiography revealed left ventricular ejection fraction of 50% with no regional wall motion abnormalities. This morning, the patient had new, sudden-onset, right lower extremity pain. He has never had pain in that extremity before. The patient has a history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Current medications include aspirin, clopidogrel, rosuvastatin, metoprolol, losartan, isosorbide mononitrate, basal-bolus insulins, and subcutaneous heparin at a prophylactic dose. The patient is a former smoker with a 30-pack-year history. Temperature is 37.6 C (99.7 F) , blood pressure is 138/84 mm Hg, pulse is 96/min, and respirations are 18/min. Physical examination reveals normal jugular venous pressure, clear lungs, no heart murmurs, and a soft, nontender abdomen. The right leg is tender and cool to the touch when compared to the left leg. Right lower extremity distal pulses are diminished, but capillary refill is intact. Left leg examination is normal with the exception of healed scars from previous saphenous vein harvesting. Neurological examination is normal. Laboratory results are as follows: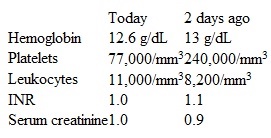 Analgesics and other supportive measures are provided, and vascular surgery is consulted. Diagnostic studies are performed, but the results are pending. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
Analgesics and other supportive measures are provided, and vascular surgery is consulted. Diagnostic studies are performed, but the results are pending. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
A) Continue current therapy and await confirmatory test results
B) Discontinue heparin and anticoagulate with oral warfarin
C) Discontinue heparin and begin intravenous direct thrombin inhibitor
D) Discontinue heparin and monitor closely
E) Switch heparin to intravenous therapeutic dosing
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q440: A 65-year-old man is brought to the
Q441: A 62-year-old hospitalized man is evaluated for
Q442: A 54-year old Caucasian man comes to
Q443: A 68-year-old woman comes to the office
Q444: A 67-year-old man comes to the physician
Q446: Imaging studies show the presence of colonic
Q447: A 46-year-old Caucasian female is hospitalized for
Q448: A 66-year-old woman comes to the office
Q449: A 30-year-old woman comes to the office
Q450: A 24-year-old man is carried into the
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents