Passage
Umami is one of five basic tastes that humans recognize, and it is triggered by L-amino acids as well as some synthetic ingredients and organic acids. Three common umami tastant molecules are shown in Figure 1.
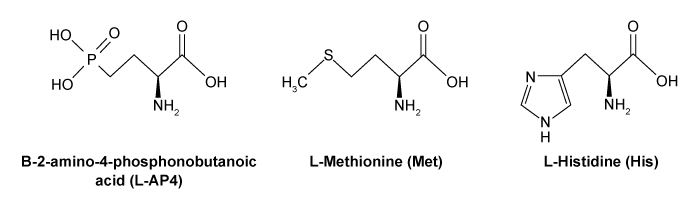 Figure 1 Three common tastant molecules known to trigger the umami taste sensationUmami taste signals are triggered upon binding of tastant molecules to the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) heterodimer T1R1-T1R3, which ultimately causes the breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) into the messenger molecules inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG) . IP3 triggers the release of Ca2+ cations and the subsequent gating of the taste-transduction channels (Figure 2) .
Figure 1 Three common tastant molecules known to trigger the umami taste sensationUmami taste signals are triggered upon binding of tastant molecules to the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) heterodimer T1R1-T1R3, which ultimately causes the breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) into the messenger molecules inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG) . IP3 triggers the release of Ca2+ cations and the subsequent gating of the taste-transduction channels (Figure 2) .
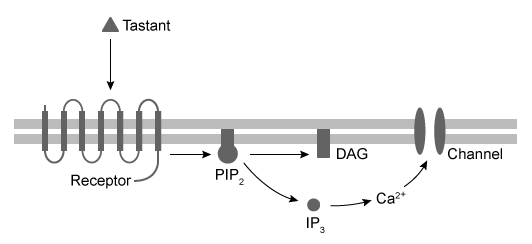 Figure 2 Signal pathway for transduction of umami taste sensationInosine monophosphate (IMP) has been suggested as enhancing (potentiating) the response of T1R1+T1R3 GPCRs to umami tastant molecules. Scientists tested this hypothesis by culturing receptors from human embryonic kidney (HEK) cells containing promiscuous G proteins. The HEK cells were then stimulated with umami tastants in the presence or absence of IMP. In each test, the cells were exposed to the same amounts of amino acid tastant and IMP. The number of cells that responded to each tastant was measured using a calcium indicator dye (FURA-2AM) in conjunction with fluorescence microscopy. By comparing the cellular response ratio of the stimulated to unstimulated HEK cells, the extent of potentiation can be assessed. The results are shown in Figure 3.
Figure 2 Signal pathway for transduction of umami taste sensationInosine monophosphate (IMP) has been suggested as enhancing (potentiating) the response of T1R1+T1R3 GPCRs to umami tastant molecules. Scientists tested this hypothesis by culturing receptors from human embryonic kidney (HEK) cells containing promiscuous G proteins. The HEK cells were then stimulated with umami tastants in the presence or absence of IMP. In each test, the cells were exposed to the same amounts of amino acid tastant and IMP. The number of cells that responded to each tastant was measured using a calcium indicator dye (FURA-2AM) in conjunction with fluorescence microscopy. By comparing the cellular response ratio of the stimulated to unstimulated HEK cells, the extent of potentiation can be assessed. The results are shown in Figure 3.
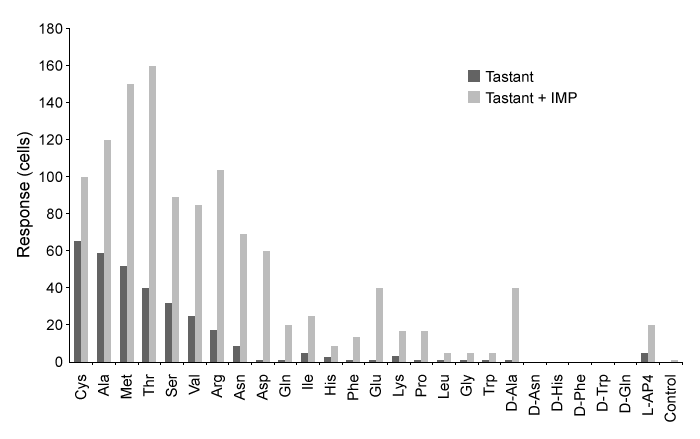 Figure 3 Quantification of amino-acid responses for T1R1+T1R3 with and without IMP
Figure 3 Quantification of amino-acid responses for T1R1+T1R3 with and without IMP
Adapted from Nelson G, Chandrashekar J, Hoon MA, et al. An amino-acid taste receptor. Nature. 2002;416(6877) :199-202.
-Which of the following best explains the results regarding D-amino acids in Figure 3?
A) D-amino acids are not as abundant in HEK cells as L-amino acids.
B) D-amino acids do not fluoresce upon addition of FURA-2AM dye.
C) D-amino acids do not trigger the formation of DAG.
D) Most D-amino acids do not effectively bind to the GPCR heterodimer T1R1+T1R3.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q24: Passage
Catabolism is an oxidative process in which
Q25: Passage
In polluted urban environments, airborne proteins can
Q26: Passage
Catabolism is an oxidative process in which
Q27: Passage
In polluted urban environments, airborne proteins can
Q28: Passage
Umami is one of five basic tastes
Q30: Passage
Depending on the active compound's specific method
Q31: Passage
Catabolism is an oxidative process in which
Q32: Passage
Depending on the active compound's specific method
Q33: Passage
Umami is one of five basic tastes
Q34: Passage
Catabolism is an oxidative process in which
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents