IL-33 is a cytokine known as an 'alarmin'. Following stimulation by pathogens or allergens, or in response to damage, epithelial cells in the skin, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract will release IL-33. This cytokine binds to its receptor, which is expressed on several cell types important in type 2 immune responses. When mice are injected with recombinant IL-33 once per day for 7 days (or saline as a control), specific cytokines are found elevated in multiple tissues and in their serum. An example of data from lung is shown in Figure Q26)A, with cytokine mRNA being measured by RT-PCR. Other cytokines, such as IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, IL-12, TNF- , and IFN- were not altered by IL-33 injection. 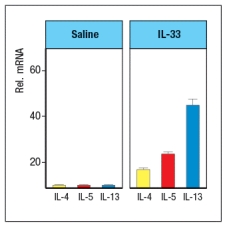
a) Name three cell types that are likely to express IL-33 receptors.
These experiments were repeated using Rag-deficient mice, in comparison to wild-type controls. When cytokines were analyzed after IL-33 treatment of Rag-deficient mice, similar amounts of the same cytokines were observed as seen in wild-type controls.
b) Do these data affect your answer to part (a) above? Why or why not?
When IL-33-deficient mice were compared to wild-type controls in a mouse model of chronic airway inflammation, disease symptoms were reduced in IL33-/- mice. In this model, chicken ovalbumin protein (OVA) is mixed with a TH2-inducing adjuvant, and used to sensitize mice by intraperitoneal injection. Four weeks later, mice are challenged intranasally with OVA or saline alone on days 28, 29, and 30. The number of cells in the bronchiolar lavage fluid is then assessed, as shown in Figure . 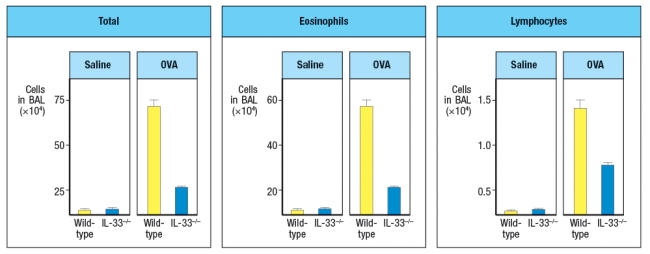
c) Given these data, as well as the cytokine data above, what are two important functions of IL-33?
Leukocytes are isolated from the lung epithelium of wild-type mice in which chronic airway inflammation has been induced to OVA. The cells are separated into two subsets: lymphocytes and non-lymphocytes. Then each population is stimulated in vitro with IL-33 in the presence or absence of OVA protein, and 48 hours later the cytokines in the supernatants are assessed by ELISA. The results are shown in Figure for one cytokine. Similar data were obtained for IL-9 and IL-13.
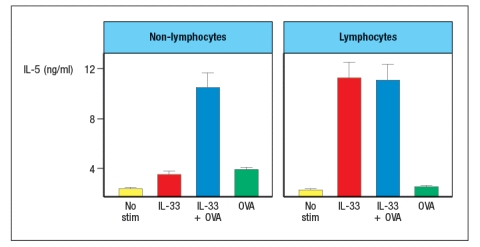
d) What are the likely cell types responding in each isolated population?
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q16: Genetic studies have identified more than 40
Q17: Genetic variations in proteins involved in immune
Q18: Red blood cells are common targets
Q19: Individuals with allergic responses to inhaled antigens
Q20: In mice, an allergic response in the
Q21: Celiac disease occurs when an individual
Q22: T-bet and GATA-3 are transcription factors
Q24: On occasion, individuals on antibiotics such
Q25: The response of most individuals to
Q26: Hypersensitivity responses to divalent cations such as
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents