A mutant B cell line is examined by confocal microscopy after incubation with a microbial pathogen recognized by the BCR on these B cells. The B cells have been stained with antibodies to visualize the localization of polymerized actin and microtubules. As a control, wild-type B cells are examined. The results are shown in Figure, with the numbers indicating the proportion of cells examined that show each pattern of staining. 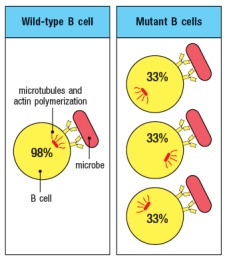
To identify the specific signaling defect in these mutant B cells, a reasonable biochemical assay would be to:
A) Determine if BCR stimulation of mutant B cells produces enhanced binding of the B cell to the microbe
B) Determine whether the mutant B cells have reduced levels of the enzyme Protein kinase C-
C) Determine whether the mutant B cells are overexpressing the enzyme Vav
D) Determine whether BCR stimulation of mutant B cells promotes exchange of GDP for GTP on cdc42
E) Determine whether BCR stimulation of mutant B cells produces increased levels of DAG
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q16: Human patients with genetic defects that result
Q17: The TCR and BCR are each composed
Q18: Scaffold proteins are often phosphorylated at multiple
Q19: Diacyl-glycerol (DAG) is one of the
Q20: The LAT:Gads:SLP-76 complex that assembles following TCR
Q22: Unlike TCR signaling, B cell receptor (BCR)
Q23: Antigen receptor signaling and lymphocyte activation.antibody
Q24: T cells with defective TCR signaling
Q25: Phosphorylation of signaling proteins can have activating
Q26: Humans with defective expression of the
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents