A 36-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of worsening shortness of breath and cough for 4 days. Her medical problems include rheumatoid arthritis, interstitial lung disease on home oxygen, and pulmonary hypertension. Her trachea is cannulated because of respiratory distress and central venous access is obtained.
In the intensive care unit, her temperature is 37.2 C (99 F) , blood pressure is 99/67 mm Hg, and pulse is 120 /min. The patient's pulse oximetry shows 100% on assist control mode with tidal volumes of 300 mL, respiratory rate of 20/min, fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) of 100%, and positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) of 5 cm H2O. Examination reveals right-sided crackles and decreased breath sounds on the left. Heart sounds are regular with a loud second heart sound. The abdomen is soft and non-tender. Examination shows no peripheral edema.
Laboratory values are as follows:
A chest radiograph is performed.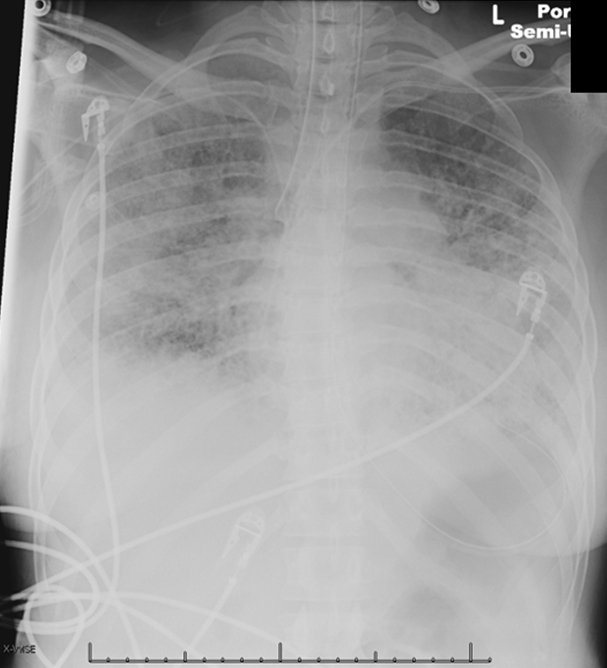
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
A) Increase PEEP
B) Increase tidal volume
C) Insert a chest tube
D) Reposition the endotracheal tube
E) Suction respiratory secretions
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q91: A 68-year-old woman is evaluated in the
Q92: A 70-year-old woman is brought to the
Q93: A 79-year-old man on mechanical ventilation is
Q94: A 55-year-old woman is hospitalized for shortness
Q95: A 43-year-old man with alcoholic pancreatitis is
Q97: A 65-year-old woman with a history of
Q98: A 63-year-old man with chronic obstructive pulmonary
Q99: A 65-year-old woman with a history of
Q100: A 60-year-old woman is brought to the
Q101: A 64-year-old woman was found poorly responsive
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents